Intercellular communication: diverse structures for exchange of genetic information
- PMID: 22510790
- PMCID: PMC3738855
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3335
Intercellular communication: diverse structures for exchange of genetic information
Abstract
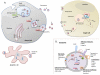
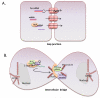
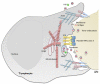
An emerging concept is that cellular communication in mammals can be mediated by the exchange of genetic information, mainly in the form of microRNAs. This can occur when extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, secreted by a donor cell are taken up by an acceptor cell. Transfer of genetic material can also occur through intimate membrane contacts between donor and acceptor cells. Specialized cell-cell contacts, such as synapses, have the potential to combine these modes of genetic transfer.
Figures
References
-
- Brosnan CA, Voinnet O. Cell-to-cell and long-distance siRNA movement in plants: mechanisms and biological implications. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2011;14:580–7. - PubMed
-
- Dunoyer P, et al. Small RNA duplexes function as mobile silencing signals between plant cells. Science. 2010;328:912–6. - PubMed
-
- Molnar A, et al. Small silencing RNAs in plants are mobile and direct epigenetic modification in recipient cells. Science. 2010;328:872–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

