Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial mitotic fission permits hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and offers a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 22511751
- PMCID: PMC3539779
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.263848
Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial mitotic fission permits hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and offers a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
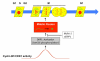
Rationale: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a lethal syndrome characterized by pulmonary vascular obstruction caused, in part, by pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) hyperproliferation. Mitochondrial fragmentation and normoxic activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) have been observed in PAH PASMCs; however, their relationship and relevance to the development of PAH are unknown. Dynamin-related protein-1 (DRP1) is a GTPase that, when activated by kinases that phosphorylate serine 616, causes mitochondrial fission. It is, however, unknown whether mitochondrial fission is a prerequisite for proliferation.
Objective: We hypothesize that DRP1 activation is responsible for increased mitochondrial fission in PAH PASMCs and that DRP1 inhibition may slow proliferation and have therapeutic potential.
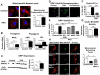
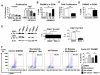
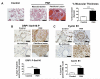
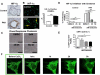
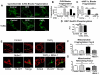
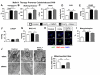
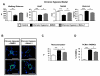
Methods and results: Experiments were conducted using human control and PAH lungs (n=5) and PASMCs in culture. Parallel experiments were performed in rat lung sections and PASMCs and in rodent PAH models induced by the HIF-1α activator, cobalt, chronic hypoxia, and monocrotaline. HIF-1α activation in human PAH leads to mitochondrial fission by cyclin B1/CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of DRP1 at serine 616. In normal PASMCs, HIF-1α activation by CoCl(2) or desferrioxamine causes DRP1-mediated fission. HIF-1α inhibition reduces DRP1 activation, prevents fission, and reduces PASMC proliferation. Both the DRP1 inhibitor Mdivi-1 and siDRP1 prevent mitotic fission and arrest PAH PASMCs at the G2/M interphase. Mdivi-1 is antiproliferative in human PAH PASMCs and in rodent models. Mdivi-1 improves exercise capacity, right ventricular function, and hemodynamics in experimental PAH.
Conclusions: DRP-1-mediated mitotic fission is a cell-cycle checkpoint that can be therapeutically targeted in hyperproliferative disorders such as PAH.
Figures
Comment in
-
Novel role for the regulation of mitochondrial fission by hypoxia inducible factor-1α in the control of smooth muscle remodeling and progression of pulmonary hypertension.Circ Res. 2012 May 25;110(11):1395-7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.270801. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22628570 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lane KB, Machado RD, Pauciulo MW, Thomson JR, Phillips JA, 3rd, Loyd JE, Nichols WC, Trembath RC. Heterozygous germline mutations in bmpr2, encoding a tgf-beta receptor, cause familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Nat Genet. 2000;26:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Thomson JR, Machado RD, Pauciulo MW, Morgan NV, Humbert M, Elliott GC, Ward K, Yacoub M, Mikhail G, Rogers P, Newman J, Wheeler L, Higenbottam T, Gibbs JS, Egan J, Crozier A, Peacock A, Allcock R, Corris P, Loyd JE, Trembath RC, Nichols WC. Sporadic primary pulmonary hypertension is associated with germline mutations of the gene encoding bmpr-ii, a receptor member of the tgf-beta family. J Med Genet. 2000;37:741–745. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Archer SL, Marsboom G, Kim GH, Zhang HJ, Toth PT, Svensson EC, Dyck JR, Gomberg-Maitland M, Thebaud B, Husain AN, Cipriani N, Rehman J. Epigenetic attenuation of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase 2 in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A basis for excessive cell proliferation and a new therapeutic target. Circulation. 2010;121:2661–2671. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

