Systemic isotretinoin therapy normalizes exaggerated TLR-2-mediated innate immune responses in acne patients
- PMID: 22513780
- PMCID: PMC3614089
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2012.111
Systemic isotretinoin therapy normalizes exaggerated TLR-2-mediated innate immune responses in acne patients
Abstract
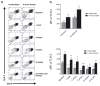
Retinoids are used in the treatment of inflammatory skin diseases and malignancies, but studies characterizing the in vivo actions of these drugs in humans are lacking. Isotretinoin is a pro-drug for all-trans retinoic acid, which can induce long-term remissions of acne; however, its complete mechanism of action is unknown. We hypothesized that isotretinoin induces remission of acne by normalizing the innate immune response to the commensal bacterium Propionibacterium acnes. Compared with normal subjects, peripheral blood monocytes from acne patients expressed significantly higher levels of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2) and exhibited significantly greater induction of TLR-2 expression following P. acnes stimulation. Treatment of patients with isotretinoin significantly decreased monocyte TLR-2 expression and subsequent inflammatory cytokine response to P. acnes after 1 week of therapy. This effect was sustained 6 months following cessation of therapy, indicating that TLR-2 modulation may be involved in the durable therapeutic response to isotretinoin. This study demonstrates that isotretinoin exerts immunomodulatory effects in patients and sheds light on a potential mechanism for its long-term effects on acne. The modulation of TLR-2 expression on monocytes has important implications in other inflammatory disorders characterized by TLR-2 dysregulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


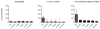
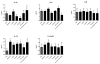
References
-
- Buchan P, Eckhoff C, Caron D, Nau H, Shroot B, Schaefer H. Repeated topical administration of all-trans-retinoic acid and plasma levels of retinoic acids in humans. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1994;30:428–434. - PubMed
-
- Candia L, Marquez J, Hernandez C, Zea AH, Espinoza LR. Toll-like receptor-2 expression is upregulated in antigen-presenting cells from patients with psoriatic arthritis: a pathogenic role for innate immunity? The Journal of rheumatology. 2007;34:374–379. - PubMed
-
- Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nature medicine. 2004;10:942–949. - PubMed
-
- Do JE, Kwon SY, Park S, Lee ES. Effects of vitamin D on expression of Toll-like receptors of monocytes from patients with Behcet’s disease. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 2008;47:840–848. - PubMed
-
- Fathy A, Mohamed RW, Ismael NA, El-Akhras MA. Expression of toll-like receptor 2 on peripheral blood monocytes of patients with inflammatory and noninflammatory acne vulgaris. Egypt J of Immun. 2009;16:127–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

