Combined DTP-HBV-HIB vaccine versus separately administered DTP-HBV and HIB vaccines for primary prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenzae B (HIB)
- PMID: 22513932
- PMCID: PMC11440342
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005530.pub3
Combined DTP-HBV-HIB vaccine versus separately administered DTP-HBV and HIB vaccines for primary prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenzae B (HIB)
Abstract
Background: Advantages to combining childhood vaccines include reducing the number of visits, injections and patient discomfort, increasing compliance and optimising prevention. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that routine infant immunisation programmes include a vaccination against Haemophilus influenzae (H. influenzae) type B (HIB) in the combined diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis (DTP)-hepatitis B virus (HBV) vaccination. The effectiveness and safety of the combined vaccine should be carefully and systematically assessed to ensure its acceptability by the community.
Objectives: To compare the effectiveness of combined DTP-HBV-HIB vaccines versus combined DTP-HBV and separate HIB vaccinations.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2011, Issue 4), which contains the Cochrane Acute Respiratory Infections Group's Specialised Register, MEDLINE (January 1966 to week 1, November 2011), EMBASE (January 1990 to November 2011) and www.clinicaltrials.gov (up to April 2011).
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or quasi-RCTs comparing vaccination with any combined DTP-HBV-HIB vaccine, with or without three types of inactivated polio virus (IPV) or concomitant oral polio vaccine (OPV) in any dose, preparation or time schedule, compared with separate vaccines or placebo, administered to infants up to two years old.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently inspected references identified by the searches and evaluated them against the inclusion criteria, extracted data and assessed the methodological quality of included trials.
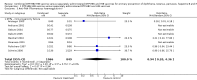
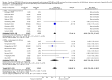
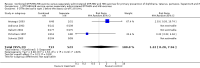
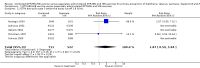
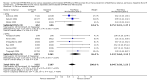
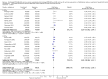
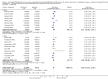
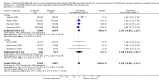
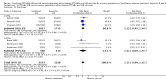
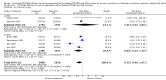
Main results: Data for the primary outcome (prevention of disease) were lacking. We performed a meta-analysis to pool the results of 20 studies with 5874 participants in an immunogenicity analysis and 5232 participants in the reactogenicity analysis. There were no data on clinical outcomes for the primary outcome (prevention of disease) and all studies used immunogenicity and reactogenicity (adverse events). The number of vaccine doses differed significantly between the studies. Heterogeneous interventions, study location, healthcare environment and combining research across disparate geographical locations, may have lead to bias. The risk of bias was unclear across most of the included studies. Comparisons found little heterogeneity. In two immunological responses the combined vaccine achieved lower responses than the separate vaccines for HIB and tetanus. No significant differences in immunogenicity were found for pertussis, diphtheria, polio and hepatitis B. Serious adverse events were comparable with mainly hospitalisation and acute bronchiolitis cases. Minor adverse events such as pain and redness were more common in children given the combined vaccine. Overall, the direction shown by the results is in favour of the DTPw (diptheria-tetanus-whole cell pertussis)-HBV-HIB vaccine rather than the DTPa (diptheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis)-HBV-HIB vaccine when compared to the separate vaccines (size of effect: risk ratio (RR) 1.43; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.98 to 2.10, for 5269 participants).
Authors' conclusions: We could not conclude that the immune responses elicited by the combined vaccine were different from or equivalent to the separate vaccines. There was significantly less immunological response for HIB and tetanus and more local reactions in the combined injections. However, these differences rely mostly on one study each. Studies did not use an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis and we were uncertain about the risk of bias in many of the studies. These results are therefore inconclusive. Studies addressing clinical end points whenever possible, using correct methodology and a large enough sample size should be conducted.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures


















Update of
-
Combined DTP-HBV-HIB vaccine versus separately administered DTP-HBV and HIB vaccines for primary prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenzae B (HIB).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Jul 8;(3):CD005530. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005530.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Apr 18;(4):CD005530. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005530.pub3. PMID: 19588375 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aristegui 2003 {published data only}
-
- Aristegui J, Dal‐Re R, Diez‐Delgado J, Mares J, Casanovas JM, Garcia‐Corbeira P, et al. Comparison of the reactogenicity and immunogenicity of a combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated polio (DTPa‐HBV‐IPV) vaccine, mixed with the Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine and administered as a single injection, with the DTPa‐IPV/Hib and hepatitis B vaccines administered in two simultaneous injections to infants at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. Vaccine 2003;21(25‐6):3593‐600. - PubMed
Avdicova 2002 {published data only}
-
- Avdicova M, Prikazsky V, Hudeckova H, Schuerman L, Willems P. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a novel hexavalent DTPa‐HBV‐IPV/Hib vaccine compared to separate concomitant injections of DTPa‐IPV/Hib and HBV vaccines, when administered according to a 3, 5 and 11 month vaccination schedule. European Journal of Pediatrics 2002;161(11):581‐7. - PubMed
Bravo 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bravo L, Carlos J, Gatchalian S, Borja‐Tabora C, Bibera G, Willems P, et al. The new DTPw‐HBV‐Hib combination vaccine can be used at the WHO schedule with a monovalent dose of hepatitis B vaccine at birth. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1998;29(4):772‐8. - PubMed
Faingezicht 2002 {published data only}
-
- Faingezicht I, Avila‐Aguerro ML, Cervantes Y, Fourneau M, Clemens SA. Primary and booster vaccination with DTPw‐HB/Hib pentavalent vaccine in Costa Rican children who had received a birth dose of hepatitis b vaccine. Pan American Journal of Public Health 2002;12(4):247‐57. - PubMed
Gabutti 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gabutti G, Zepp F, Schuerman L, Dentico P, Bamfi F, Soncini R, et al. Evaluation of the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a DTPa‐HBV‐IPV combination vaccine co‐administered with a Hib conjugate vaccine either as a single injection of a hexavalent combination or as two separate injections at 3, 5 and 11 months of age. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2004;36(8):585‐92. - PubMed
Gabutti 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gabutti G, Bona G, Dentico P, Bamfi F, Hardt K, Majori S, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity following primary immunisation with a combined DTaP‐HBV vaccine and a Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine administered by separate or mixed injection. Clinical Drug Investigation 2005;25(5):315‐23. - PubMed
Greenberg 2000 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg DP, Wong VK, Partridge S, Chang SJ, Jing J, Howe BJ, et al. Immunogenicity of a Haemophilus influenzae type b‐tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine when mixed with a diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐hepatitis B combination vaccine. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2000;19(12):1135‐40. - PubMed
Mallet 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mallet E, Fabre P, Pines E, Salomon H, Staub T, Schodel F, et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a new liquid hexavalent combined vaccine compared with separate administration of reference licensed vaccines in infants. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2000;19(12):1119‐27. - PubMed
Marshall 2010 {published data only}
-
- Marshall H, McIntyre P, Roberton D, Dinan L, Hardt K. Primary and booster immunization with a diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B (DTPa‐HBV) and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine administered separately or together is safe and immunogenic. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2010;14(1):e41‐9. [PUBMED: 19467896] - PubMed
Nolan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Nolan T, Hogg G, Darcy MA, Skeljo M, Carlin J, Boslego J. A combined liquid Hib (PRP‐OMPC), hepatitis B, diphtheria, tetanus and whole‐cell pertussis vaccine: controlled studies of immunogenicity and reactogenicity. Vaccine 2001;19(15‐16):2127‐37. - PubMed
Omenaca 2001 {published data only}
-
- Omenaca F, Dal‐Re R, D'Apuzzo V, Kattamis C, Gnehm HP, Garcia‐Sicilia J, et al. Reactogenicity of DTPa‐HBV/Hib vaccine administered as a single injection vs DTPa‐HBV and Hib vaccines administered simultaneously at separate sites, to infants at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. Vaccine 2001;19(30):4260‐6. - PubMed
Ortega‐Barria 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ortega‐Barria E, Kanra G, Leroux G, Bravo L, Safary A, Levlevre I. The immunogenicity and reactogenicity of DTPw‐HBV/Hib 2.5 combination vaccine: Results from four phase III multicenter trials across three continents. Vaccine 2007;25(50):8432‐40. - PubMed
Pichichero 1997 {published data only}
-
- Pichichero ME, Passador S. Administration of combined diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and pertussis vaccine, hepatitis B vaccine, and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine to infants and response to a booster dose of Hib conjugate vaccine. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1997;25(6):1378‐84. - PubMed
Ramkissoon 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ramkissoon A, Coovadia HM, Jugnundan P, Willems P, Clemens BR. A new combined DTP‐HBV‐Hib vaccine‐strategy for incorporation of Hib vaccination into childhood immunisation programmes. South African Medical Journal 2001;91(10):864‐9. - PubMed
Rao 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rao R, Dhingra MS, Bavdekar S, Behera N, Daga SR, Dutta AK, et al. A comparison of immunogenicity and safety of indigenously developed liquid (DTwPHB‐Hib) pentavalent combination vaccine (Shan 5) with Easyfive (liq) and TritanrixHB + Hiberix (lyo) in Indian infants administered according to the EPI schedule. Human vaccines 2009;5(6):425‐9. [PUBMED: 19333002] - PubMed
Riedemann 2002 {published data only}
-
- Riedemann S, Reinhardt G, Jara J, Rios R, Wenzel MS, Willems P, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of combined versus separately administered DTPw‐HBV and Hib vaccines given to healthy infants at 2, 4, and 6 months of age, with a booster at 18 months. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2002;6(3):215‐22. - PubMed
Santos 2002 {published data only}
-
- Santos JI, Martin A, Leon T, Rivera L, Gaitan ME, Rio C, et al. DTPw‐HB and Hib primary and booster vaccination: combined versus separate administration to Latin American children. Vaccine 2002;20(13‐14):1887‐93. - PubMed
Schmitt 2000 {published data only}
-
- Schmitt HJ, Knuf M, Ortiz E, Sanger R, Uwamwezi MC, Kaufhold A. Primary vaccination of infants with diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐hepatitis B virus‐ inactivated polio virus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines given as either separate or mixed injections. Journal of Pediatrics 2000;137(3):304‐12. - PubMed
Tregnaghi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tregnaghi M, Lopez P, Rocha C, Rivera L, David M, Ruttimann R. A new DTPw‐HB/Hib combination vaccine for primary and booster vaccination of infants in Latin America. Pan American Journal of Public Health 2006;19(3):179‐88. - PubMed
Win 1997 {published data only}
-
- Win KM, Aye M, Htay‐Htay H, Safary A, et al. Comparison of separate and mixed administration of DTPw‐HBV and Hib vaccines: Immunogenicity and reactogenicity profiles. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 1997;2(2):79‐84.
References to studies excluded from this review
Aristegui 1998 {published data only}
-
- Aristegui J, Dal‐Re R, Garrote E, Gonzalez A, Arrate JP, Perez A. Assessment of the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a quadrivalent diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis and hepatitis B (DTPa‐HBV) vaccine administered in a single injection with Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine, to infants at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. Vaccine 1998;16(20):1976‐81. - PubMed
Aristegui 2001 {published data only}
-
- Aristegui J, Garcia‐Corbeira P, De‐la‐Flor J, Dal‐Re R, Mares J, Moraga F, et al. Reactogenicity and safety of DTPa vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (Hib) in a single injection vs DTPw and Hib as separate injections as a booster vaccination in 18‐month‐old children. Clinical Drug Investigation 2001;21(1):9‐16.
Bavdekar 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bavdekar SB, Maiya PP, Subba Rao SD, Bock HL. Immunogenicity and safety of combined diphtheria tetanus whole cell pertussis hepatitis B/ Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine in Indian infants. Indian Pediatrics 2007;44(7):505‐10. - PubMed
Botet‐Asensi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Botet‐Asensi FI, Veronese A, Carmen Otero M, Desamparados Tamarit Perez M, Hontangas Lopez JL, Viviani S. Immunogenicity and safety in infants of a DTwPHib full liquid vaccine. Acta Pediatrica 2003;92(5):541‐5. - PubMed
Calbo 2002 {published data only}
-
- Calbo F, Dal Re R, Diez Delgado J, Ona S, Sanchez Prados F, Garcia Corbeira P, et al. Comparative trial to assess the reactogenicity of the diphtheria‐tetanusacellular pertussis (DTPa) vaccine plus Haemophilus influenza type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine and that of the diphtheria‐tetanus‐whole cell pertussis (DTPw) vaccine plus Hib conjugate vaccine, administered in single injection as a booster dose to 14‐20 months‐old children. Medicina Clinica 2002;118(1):1‐4. - PubMed
Clemens 2003 {published data only}
-
- Clemens SC, Azevedo T, Homma A. Feasibility study of the immunogenicity and safety of a novel DTPw/Hib (PRP‐T) Brazilian combination compared to a licensed vaccine in healthy children at 2, 4, and 6 months of age. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medicina Tropical 2003;36(3):321‐30. - PubMed
Denoel 2007 {published data only}
Diaz‐Mitoma 2011 {published data only}
-
- Diaz‐Mitoma F, Halperin SA, Tapiero B, Hoffenbach A, Zappacosta PS, Radley D, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of three different formulations of a liquid hexavalent diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐inactivated poliovirus‐Haemophilus influenzae b conjugate‐hepatitis B vaccine at 2, 4, 6 and 12‐14 months of age. Vaccine 2011;29(6):1324‐31. - PubMed
Gatchalian 2005 {published data only}
-
- Gatchalian S, Reyes M, Bernal N, Lefevre I, David MP, Han HH, et al. A new DTPw‐HBV/Hib vaccine is immunogenic and safe when administered according to the EPI (Expanded Programme for Immunization) schedule and following hepatitis B vaccination at birth. Human Vaccines 2005;1(5):198‐203. - PubMed
Gentile 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gentile A, Umido V, Czerniuk P, Nacul J, Seigelchifer M, Hilbert AK, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a combined fully liquid DTPw‐HepB‐Hib pentavalent vaccine in healthy infants: No clinically relevant impact of a birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2011;15(1):e24‐e9. - PubMed
Gylca 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gylca R, Gylca V, Benes O, Melnic A, Chicu V, Weisbecker C, et al. A new DTPa‐HBV‐IPV vaccine co‐administered with Hib, compared to a commercially available DTPw‐IPV/Hib vaccine co‐administered with HBV, given at 6, 10 and 14 weeks following HBV at birth. Vaccine 2001;19(7‐8):825‐33. - PubMed
Halperin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Halperin SA, Tapiero B, Diaz‐Mitoma F, Law B, Hoffenbach J, Zappacosta A, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a hexavalent diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐inactivated poliovirus‐Haemophilus influenzae b conjugate‐hepatitis B vaccine at 2, 3, 4, and 12‐14 months of age. Vaccine 2009;27(19):2540‐7. - PubMed
Hla 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hla KH, Thein SA, Aye A, Han HH, Bock HL, David MP, et al. Reactogenicity and immunogenicity profiles of a novel pentavalent diphtheria‐tetanus‐whole cell pertussis‐hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine: a randomised dose‐ranging trial of the Hib tetanus‐conjugate content. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2006;25(8):706‐12. - PubMed
Hogg 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hogg K, Hogg G. The immunogenicity of oral poliomyelitis vaccine in a primary vaccination series at 2, 4 and 6 months given concurrently with Hib, hepatitis B and diphtheria, tetanus and whole‐cell pertussis vaccines administered as three separate injections or as a combination pentavalent vaccine. Vaccine 2003;21(21‐2):2906‐10. - PubMed
Huang 1998 {published data only}
-
- Huang LM, Chang PF, Lee PI, Chiu HH, Tsai SY, Lee CY. Immunogenicity and safety of Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine (HibTITER) and a combination vaccine of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and HibTITER (TETRAMUNE) in two‐month‐old infants. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection 1998;31(3):180‐6. - PubMed
Kalies 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kalies H, Verstraeten T, Grote V, Meyer N, Siedler A, Schmitt HJ, et al. Four and one‐half‐year follow‐up of the effectiveness of diphtheria‐tetanus toxoids‐acellular pertussis/Haemophilus influenzae type b and diphtheria‐tetanus toxoids‐acellular pertussis‐inactivated poliovirus/H. influenzae type b combination vaccines in Germany. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2004;23(10):944‐50. - PubMed
Kanra 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kanra G, Kara A, Demiralp O, Contorni M, Hilbert AK, Spyr C, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a new fully liquid DTPw‐HepB‐Hib combination vaccine in infants. Human Vaccines 2006;2(4):155‐60. - PubMed
Kilpi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kilpi T, Silfverdal M, Nilsson SA, Syrjanen L, Belloni R, Desole C, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of two diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐hepatitis B‐inactivated polio virus‐Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines administered at 3, 5 and 11‐12 months of age. Human Vaccines 2009;5(1):18‐25. - PubMed
Knuf 2006 {published data only}
-
- Knuf M, Habermehl P, Cimino C, Petersen G, Schmitt HJ, Habermehl P. Immunogenicity, reactogenicity and safety of a 7‐valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) concurrently administered with a DTPa‐HBV‐IPV/Hib combination vaccine in healthy infants. Vaccine 2006;24(22):4727‐36. - PubMed
Lagos 2005 {published data only}
-
- Lagos R, Hoffenbach A, Scemama M, Dupuy M, Schodel F, Hessel L, et al. Lot‐to‐lot consistency of a combined hexavalent diptheria‐tetanus‐acellular‐pertussis, hepatitis B, Inactivated polio and haemophilus B conjugate vaccine, administered to healthy Chilean infants at two, four and six months of age. Human Vaccines 2005;1(3):112‐7. - PubMed
Lim 2007 {published data only}
-
- Lim FS, Han HH, Jacquet JM, Bock HL. Primary vaccination of infants against hepatitis B can be completed using a combined hexavalent diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐hepatitis B‐inactivated poliomyelitis‐Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore 2007;36(10):801‐6. - PubMed
Lopez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lopez P, Rubiano L, Pilar Rubio M, David MP, Safary A. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of DTPw‐HB/Hib vaccine administered to Colombian infants after a birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine. Expert Review of Vaccines 2002;1(3):277‐83. - PubMed
Madhi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Madhi SA, Mitha I, Cutland C, Groome M, Santos‐Lima E. Immunogenicity and safety of an investigational fully liquid hexavalent combination vaccine versus licensed combination vaccines at 6, 10, and 14 weeks of age in healthy South African infants. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2011;30(4):e68‐74. - PubMed
Meriste 2006 {published data only}
-
- Meriste S, Lutsar I, Tamm E, Willems P. Safety and immunogenicity of a primary course and booster dose of a combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B and inactivated poliovirus vaccine. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2006;38(5):350‐6. - PubMed
Mills 1998 {published data only}
-
- Mills E, Gold R, Thipphawong J, Barreto L, Guasparini R, Meekison W, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a combined five‐component pertussis‐diphtheria‐tetanus‐inactivated poliomyelitis‐Haemophilus B conjugate vaccine administered to infants at two, four and six months of age. Vaccine 1998;16(6):576‐85. - PubMed
Nolan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Nolan T, Altmann A, Skeljo M, Streeton C, Schuerman L. Antibody persistence, PRP‐specific immune memory, and booster responses in infants immunised with a combination DTPa‐HBV‐IPV/Hib vaccine. Vaccine 2004;23(1):14‐20. - PubMed
Pichichero 1999 {published data only}
-
- Pichichero ME, Voloshen T, Zajac D, Passador S. Avidity maturation of antibody to Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) after immunization with diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐hib‐hepatitis B combined vaccine in infants. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1999;180(4):1390‐3. - PubMed
Pichichero 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pichichero ME, Bernstein H, Blatter MM, Schuerman L, Cheuvart B, Holmes SJ. Immunogenicity and safety of a combination diphtheria, tetanus toxoid, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, and inactivated poliovirus vaccine co‐administered with a 7‐valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and a Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine. Journal of Pediatrics 2007;151(1):43‐9; e1‐2. - PubMed
Poolman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Poolman J, Kaufhold A, Grave D, Goldblatt D. Clinical relevance of lower Hib response in DTPa‐based combination vaccines. Vaccine 2001;19(17‐9):2280‐5. - PubMed
Saenger 2005 {published data only}
-
- Saenger R, Maechler G, Potreck M, Zepp F, Knuf M, Habermehl P, et al. Booster vaccination with hexavalent DTPa‐HBV‐IPV/Hib vaccine in the second year of life is as safe as concomitant DTPa‐IPV/Hib + HBV administered separately. Vaccine 2005;23(9):1135‐43. - PubMed
Scheifele 2005 {published data only}
-
- Scheifele DW, Halperin SA, Rubin E, Tapiero B, Guasparini R, Meekison W, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a pentavalent combination vaccine (diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, polio and haemophilus influenzae type B conjugate) when administered as a fourth dose at 15 to 18 months of age. Human Vaccines 2005;1(5):180‐6. - PubMed
Scheifele 2006 {published data only}
-
- Scheifele DW, Halperin SA, Smith B, Ochnio J, Meloff K, Duarte‐Monteiro D. Assessment of the compatibility of co‐administered 7‐valent pneumococcal conjugate, DTaP.IPV/PRP‐T Hib and hepatitis B vaccines in infants 2‐7 months of age. Vaccine 2006;24(12):2057‐64. - PubMed
Tichmann 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tichmann I, Preidel H, Grunert D, Habash S, Schult R, Maier R, et al. Comparison of the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of two commercially available hexavalent vaccines administered as a primary vaccination course at 2, 4 and 6 months of age. Vaccine 2005;23(25):3272‐9. - PubMed
Tichmann‐Schumann 2005 {published data only}
-
- Tichmann‐Schumann I, Soemantri P, Behre U, Disselhoff J, Mahler H, Maechler G, et al. Immunogenicity and reactogenicity of four doses of diphtheria‐tetanus‐three‐component acellular pertussis‐hepatitis B‐inactivated polio virus‐Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine co‐administered with 7‐valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2005;24(1):70‐7. - PubMed
Tregnaghi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Tregnaghi MW, Zambrano B, Santos‐Lima E. Immunogenicity and safety of an investigational hexavalent diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis‐inactivated poliovirus‐hepatitis B‐Haemophilus influenzae B conjugate combined vaccine in healthy 2‐, 4‐, and 6‐month‐old Argentinean infants. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2011;30(6):e88‐96. - PubMed
Trollfors 2005 {published data only}
-
- Trollfors B, Taranger J, Lagergard T, Sundh V. Reduced immunogenicity of diphtheria and tetanus toxoids when combined with pertussis toxoid. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2005;24(1):85‐6. - PubMed
Usonis 1999a {published data only}
-
- Usonis V, Bakasenas V. Does concomitant injection of a combined diphtheria‐tetanus‐acellular pertussis ‐ Hepatitis B virus ‐ Inactivated polio virus vaccine influence the reactogenicity and immunogenicity of commercial Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccines?. European Journal of Pediatrics 1999;158(5):398‐402. - PubMed
Usonis 1999b {published data only}
-
- Usonis V, Bakasenas V. Evaluation of the immunogenicity and reactogenicity of a new combined diphtheria, tetanus, whole‐cell Bordetella pertussis and Hepatitis B vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine in children at 3, 4.5 and 6 months of age. Acta Medica Lituanica 1999;T6:Nr 3.
Zepp 1997 {published data only}
-
- Zepp F, Schmitt HJ, Kaufhold A, Schuind A, Knuf M, Habermehl P, et al. Evidence for induction of polysaccharide specific B‐cell‐memory in the 1st year of life: plain Haemophilus influenzae type b‐PRP (Hib) boosters children primed with a tetanus‐conjugate Hib‐DTPa‐HBV combined vaccine. European Journal of Pediatrics 1997;156(1):18‐24. - PubMed
Zepp 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zepp F, Knuf M, Heininger U, Jahn K, Collard A, Habermehl P, et al. Safety, reactogenicity and immunogenicity of a combined hexavalent tetanus, diphtheria, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, inactivated poliovirus vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine, for primary immunization of infants. Vaccine 2004;22(17‐8):2226‐33. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Sanofi‐Aventis 2011 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Sanofi‐Aventis ICMJE Investigators. Study of PENTAXIM™ Vaccine Versus TETRAXIM™ Vaccine Given With ACTHIB™ Vaccine in South Korean Infants. www.clinicaltrials.gov First Received on October 1, 2010. Last Updated on April 4, 2011.
Additional references
Ball 2001
-
- Ball LK, Falk LA, Horne D, Finn TM. Evaluating the immune response to combination vaccines. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2001;33(Suppl 4):299‐305. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
WHO 1998
-
- World Health Organization. Global Programme for Vaccines and Immunization: The WHO position paper on Haemophilus influenza type b conjugate vaccines. Weekly Epidemiological Record 1998;73(10):64‐71. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Bar‐On 2009
-
- Bar‐On ES, Goldberg E, Fraser A, Vidal L, Hellmann S, Leibovici L. Combined DTP‐HBV‐HIB vaccine versus separately administered DTP‐HBV and HIB vaccines for primary prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B and Haemophilus influenzae B (HIB). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005530.pub2] - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

