Micro-Raman spectroscopy of silver nanoparticle induced stress on optically-trapped stem cells
- PMID: 22514708
- PMCID: PMC3325966
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035075
Micro-Raman spectroscopy of silver nanoparticle induced stress on optically-trapped stem cells
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2012;7(7): doi/10.1371/annotation/60f68765-e790-4ab1-b1f2-3867100c6e3e
Abstract
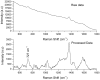
We report here results of a single-cell Raman spectroscopy study of stress effects induced by silver nanoparticles in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). A high-sensitivity, high-resolution Raman Tweezers set-up has been used to monitor nanoparticle-induced biochemical changes in optically-trapped single cells. Our micro-Raman spectroscopic study reveals that hMSCs treated with silver nanoparticles undergo oxidative stress at doping levels in excess of 2 µg/ml, with results of a statistical analysis of Raman spectra suggesting that the induced stress becomes more dominant at nanoparticle concentration levels above 3 µg/ml.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


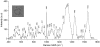


References
-
- Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim J-H, Park SJ, et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine. 2007;3:95–101. - PubMed
-
- Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27:76–83. - PubMed
-
- Durán N, Marcato PD, De Conti R, Alves OL, Costab FTM, et al. Potential use of silver nanoparticles on pathogenic bacteria, their toxicity and possible mechanisms of action. J Braz Chem Soc. 2010;21:949–959.
-
- Prucek R, Tucek J, Kilianová M, Panácek A, Kvítek L, et al. The targeted antibacterial and antifungal properties of magnetic nanocomposite of iron oxide and silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011;32:4704–4713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

