A prospective investigation of physical health outcomes in abused and neglected children: new findings from a 30-year follow-up
- PMID: 22515854
- PMCID: PMC3483964
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300636
A prospective investigation of physical health outcomes in abused and neglected children: new findings from a 30-year follow-up
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated whether abused and neglected children are at risk for negative physical health outcomes in adulthood.
Methods: Using a prospective cohort design, we matched children (aged 0-11 years) with documented cases of physical and sexual abuse and neglect from a US Midwestern county during 1967 through 1971 with nonmaltreated children. Both groups completed a medical status examination (measured health outcomes and blood tests) and interview during 2003 through 2005 (mean age=41.2 years).
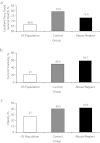
Results: After adjusting for age, gender, and race, child maltreatment predicted above normal hemoglobin, lower albumin levels, poor peak airflow, and vision problems in adulthood. Physical abuse predicted malnutrition, albumin, blood urea nitrogen, and hemoglobin A1C. Neglect predicted hemoglobin A1C, albumin, poor peak airflow, and oral health and vision problems, Sexual abuse predicted hepatitis C and oral health problems. Additional controls for childhood socioeconomic status, adult socioeconomic status, unhealthy behaviors, smoking, and mental health problems play varying roles in attenuating or intensifying these relationships.
Conclusions: Child abuse and neglect affect long-term health status-increasing risk for diabetes, lung disease, malnutrition, and vision problems-and support the need for early health care prevention.
Figures
References
-
- Shonkoff JP, Boyce WT, McEwen BS. Neuroscience, molecular biology, and the childhood roots of health disparities. JAMA. 2009;301(21):2252–2259 - PubMed
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services Child Maltreatment 2009. Administration for Children and Families; 2010. Available at: http://www.acf.hhs.gov/programs/cb/pubs/cm09. Accessed November 10, 2011
-
- Dong M, Giles WH, Felitti VJet al.Insights into causal pathways for ischemic heart disease: adverse childhood experiences study. Circulation. 2004;110(13):1761–1766 - PubMed
-
- Dubowitz H. The impact of child maltreatment on health. : Starr RH, Jr, Wolfe DA, The Effects of Child Abuse and Neglect: Issues and Research. New York: Guilford Press; 1991: 278–294
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03 AA009238/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA09238/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH049467/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA10060/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AA11108/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- HD40774/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AA011108/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA017842/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH58386/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH058386/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA17842/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD040774/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA010060/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

