Imaging tumor-stroma interactions during chemotherapy reveals contributions of the microenvironment to resistance
- PMID: 22516258
- PMCID: PMC3332002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.017
Imaging tumor-stroma interactions during chemotherapy reveals contributions of the microenvironment to resistance
Abstract
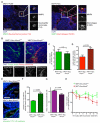
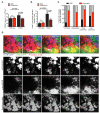
Little is known about the dynamics of cancer cell death in response to therapy in the tumor microenvironment. Intravital microscopy of chemotherapy-treated mouse mammary carcinomas allowed us to follow drug distribution, cell death, and tumor-stroma interactions. We observed associations between vascular leakage and response to doxorubicin, including improved response in matrix metalloproteinase-9 null mice that had increased vascular leakage. Furthermore, we observed CCR2-dependent infiltration of myeloid cells after treatment and that Ccr2 null host mice responded better to treatment with doxorubicin or cisplatin. These data show that the microenvironment contributes critically to drug response via regulation of vascular permeability and innate immune cell infiltration. Thus, live imaging can be used to gain insights into drug responses in situ.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
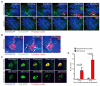
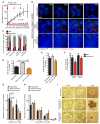
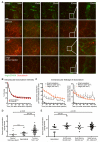
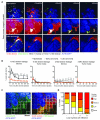


References
-
- Campiglio M, Somenzi G, Olgiati C, Beretta G, Balsari A, Zaffaroni N, Valagussa P, Menard S. Role of proliferation in HER2 status predicted response to doxorubicin. Int J Cancer. 2003;105:568–573. - PubMed
-
- Coussens LM, Fingleton B, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science. 2002;295:2387–2392. - PubMed
-
- Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:275–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

