PNGase F catalyzes de-N-glycosylation in a domestic microwave
- PMID: 22516523
- PMCID: PMC3383888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.04.011
PNGase F catalyzes de-N-glycosylation in a domestic microwave
Abstract
Common de-N-glycosylation protocols usually require a lengthy incubation time. Although pressure cycling technology or scientific microwave reactors can accelerate this enzyme reaction, they may not be easily accessible. In this brief report, we employed an alternative strategy using a standard domestic microwave oven to perform the de-N-glycosylation. Model glycoproteins (bovine RNase B, bovine fetuin, and human IgG) and a complex mixture from human plasma were fully deglycosylated in 20 min, without any apparent adverse affects on the glycans or protein backbones. This new method provides a simple and inexpensive solution to achieve rapid de-N-glycosylation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

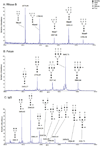
References
-
- Rudd PM, Rudan I, Wright AF. High-throughput glycome analysis is set to join high-throughput genomics. J Proteome Res. 2009;8:1105. - PubMed
-
- Sandoval WN, Arellano F, Arnott D, Raab H, Vandlen R, Lill JR. Rapid removal of N-linked oligosaccharides using microwave assisted enzyme catalyzed deglycosylation. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 2007;259:117–123.
-
- Krenkova J, Lacher NA, Svec F. Multidimensional system enabling deglycosylation of proteins using a capillary reactor with peptide-N-glycosidase F immobilized on a porous polymer monolith and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry of glycans. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216:3252–3259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

