Dendrimer-based postnatal therapy for neuroinflammation and cerebral palsy in a rabbit model
- PMID: 22517883
- PMCID: PMC3492056
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003162
Dendrimer-based postnatal therapy for neuroinflammation and cerebral palsy in a rabbit model
Abstract
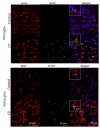
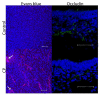
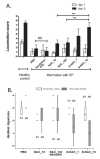
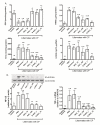
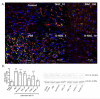
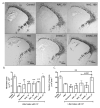
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a chronic childhood disorder with no effective cure. Neuroinflammation, caused by activated microglia and astrocytes, plays a key role in the pathogenesis of CP and disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis. Targeting neuroinflammation can be a potent therapeutic strategy. However, delivering drugs across the blood-brain barrier to the target cells for treating diffuse brain injury is a major challenge. We show that systemically administered polyamidoamine dendrimers localize in activated microglia and astrocytes in the brain of newborn rabbits with CP, but not healthy controls. We further demonstrate that dendrimer-based N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) therapy for brain injury suppresses neuroinflammation and leads to a marked improvement in motor function in the CP kits. The well-known and safe clinical profile for NAC, when combined with dendrimer-based targeting, provides opportunities for clinical translation in the treatment of neuroinflammatory disorders in humans. The effectiveness of the dendrimer-NAC treatment, administered in the postnatal period for a prenatal insult, suggests a window of opportunity for treatment of CP in humans after birth.
Figures

Comment in
-
A baby step for nano.Sci Transl Med. 2012 Apr 18;4(130):130fs8. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003934. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22517882
-
Neurological disorders: Nanoparticle opens door to cerebral palsy treatment.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 May 18;11(6):440-1. doi: 10.1038/nrd3758. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22596251 No abstract available.
-
Perinatal nanomedicine: dendrimer-based therapy for neuroinflammatory disorders.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012 Sep;7(9):1294. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2012. PMID: 23162863 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, Goldstein M, Bax M, Damiano D, Dan B, Jacobsson B. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2007;49:s109, 3–7. - PubMed
-
- Kirby RS, Wingate MS, Van Naarden Braun K, Doernberg NS, Arneson CL, Benedict RE, Mulvihill B, Durkin MS, Fitzgerald RT, Maenner MJ, Patz JA, Yeargin-Allsopp M. Prevalence and functioning of children with cerebral palsy in four areas of the United States in 2006: a report from the Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network. M. Res Dev Disabil. 2011;32:462–9. - PubMed
-
- Honeycutt A, Dunlap L, Chen H, Homsi G, Grosse S, Schendel D. Economic Costs Associated with Mental Retardation, Cerebral Palsy, Hearing Loss, and Vision Impairment - United States. Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2004;53:57–59. - PubMed
-
- Leviton A, Gilles F. Maternal urinary tract infections and fetal leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979;301:661. - PubMed
-
- Yoon BH, Romero R, Park JS, Kim CJ, Kim SH, Choi JH, Han TR. Fetal exposure to an intra-amniotic inflammation and the development of cerebral palsy at the age of three years. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2000;182:675–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

