The Design and Construction of K11: A Novel α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptide
- PMID: 22518150
- PMCID: PMC3299254
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/764834
The Design and Construction of K11: A Novel α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptide
Abstract
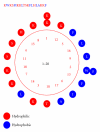
Amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides comprise a class of broad-spectrum agents that are used against pathogens. We designed a series of antimicrobial peptides, CP-P (KWKSFIKKLTSKFLHLAKKF) and its derivatives, and determined their minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, their minimum hemolytic concentrations (MHCs) for human erythrocytes, and the Therapeutic Index (MHC/MIC ratio). We selected the derivative peptide K11, which had the highest therapeutic index (320) among the tested peptides, to determine the MICs against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and 22 clinical isolates including Acinetobacter baumannii, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Klebsiella pneumonia. K11 exhibited low MICs (less than 10 μg/mL) and broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, especially against clinically isolated drug-resistant pathogens. Therefore, these results indicate that K11 is a promising candidate antimicrobial peptide for further studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of positively charged residues on the polar and non-polar faces of amphipathic α-helical antimicrobial peptides on specificity and selectivity for Gram-negative pathogens.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018 Jan;91(1):75-92. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13058. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2018. PMID: 28636788
-
Rational design of α-helical antimicrobial peptides to target Gram-negative pathogens, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: utilization of charge, 'specificity determinants,' total hydrophobicity, hydrophobe type and location as design parameters to improve the therapeutic ratio.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011 Apr;77(4):225-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2011.01086.x. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011. PMID: 21219588 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effect of two antimicrobial peptides, Nisin and P10 with conventional antibiotics against extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and colistin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates.Microb Pathog. 2021 Jan;150:104700. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104700. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33346078
-
Peptides from American alligator plasma are antimicrobial against multi-drug resistant bacterial pathogens including Acinetobacter baumannii.BMC Microbiol. 2016 Aug 19;16(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0799-z. BMC Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27542832 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of distribution and drug resistance of pathogens isolated from 541 hospitalized children with burn infection].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016 Nov 20;32(11):670-675. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.11.008. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27894388 Chinese.
Cited by
-
New linear antiplasmodial peptides related to angiotensin II.Malar J. 2015 Nov 4;14:433. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0974-y. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 26537730 Free PMC article.
-
SCMRSA: a New Approach for Identifying and Analyzing Anti-MRSA Peptides Using Estimated Propensity Scores of Dipeptides.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 1;7(36):32653-32664. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04305. eCollection 2022 Sep 13. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36120041 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in developing insect natural products as potential modern day medicines.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:904958. doi: 10.1155/2014/904958. Epub 2014 May 6. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24883072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LAMP: A Database Linking Antimicrobial Peptides.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 18;8(6):e66557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066557. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23825543 Free PMC article.
-
LAMP2: a major update of the database linking antimicrobial peptides.Database (Oxford). 2020 Jan 1;2020:baaa061. doi: 10.1093/database/baaa061. Database (Oxford). 2020. PMID: 32844169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marr AK, Gooderham WJ, Hancock RE. Antibacterial peptides for therapeutic use: obstacles and realistic outlook. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 2006;6(5):468–472. - PubMed
-
- Ganz T, Lehrer RI. Antimicrobial peptides of vertebrates. Current Opinion in Immunology. 1998;10(1):41–44. - PubMed
-
- Zasloff M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature. 2002;415(6870):389–395. - PubMed
-
- Ginsburg I, Koren E. Are cationic antimicrobial peptides also ‘double-edged swords’. Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy. 2008;6(4):453–462. - PubMed
-
- Shin SY, Lee SH, Yang ST, et al. Antibacterial, antitumor and hemolytic activities of α-helical antibiotic peptide, P18 and its analogs. Journal of Peptide Research. 2001;58(6):504–514. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous