Regional anaesthesia with sedation protocol to safely debride sacral pressure ulcers
- PMID: 22520149
- PMCID: PMC7950615
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2011.00912.x
Regional anaesthesia with sedation protocol to safely debride sacral pressure ulcers
Abstract
A treatment challenge for patients with sacral pressure ulcers is balancing the need for adequate surgical debridement with appropriate anaesthesia management. We are functioning under the hypothesis that regional anaesthesia has advantages over general anaesthesia. We describe our regional anaesthesia protocol for perioperative and postoperative management.
© 2012 The Authors. International Wound Journal © 2012 Blackwell Publishing Ltd and Medicalhelplines.com Inc.
Figures
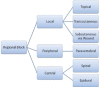

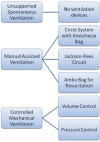


References
-
- National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (NPUAP) and European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (EPUAP). Prevention and treatment of pressure ulcers: clinical practice guideline. Washington, DC: National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, 2009.
-
- Brem H, Lyder CH. Protocol for the successful treatment of pressure ulcers. Am Surg 2004;188 Suppl:9S–17S. - PubMed
-
- Lyder CH. Pressure ulcer prevention and management. JAMA 2003;289:223–6. - PubMed
-
- Russo CA, Steiner C, Spector W. Hospitalizations related to pressure ulcers among adults 18 years and older 2006. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Brief 64. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, 2008. URL http://www.hcup‐us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb64.pdf [acce‐ssed on 21 June 2010] - PubMed
-
- Allman RM, Goode PS, Burst N, Bartolucci AA, Thomas DR. Pressure ulcers, hospital complications, and disease severity: impact on hospital costs and length of stay. Adv Wound Care 1999;12:22–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

