Nuclear functions and subcellular trafficking mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor family
- PMID: 22520625
- PMCID: PMC3418567
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-13
Nuclear functions and subcellular trafficking mechanisms of the epidermal growth factor receptor family
Abstract
Accumulating evidence suggests that various diseases, including many types of cancer, result from alteration of subcellular protein localization and compartmentalization. Therefore, it is worthwhile to expand our knowledge in subcellular trafficking of proteins, such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ErbB-2 of the receptor tyrosine kinases, which are highly expressed and activated in human malignancies and frequently correlated with poor prognosis. The well-characterized trafficking of cell surface EGFR is routed, via endocytosis and endosomal sorting, to either the lysosomes for degradation or back to the plasma membrane for recycling. A novel nuclear mode of EGFR signaling pathway has been gradually deciphered in which EGFR is shuttled from the cell surface to the nucleus after endocytosis, and there, it acts as a transcriptional regulator, transmits signals, and is involved in multiple biological functions, including cell proliferation, tumor progression, DNA repair and replication, and chemo- and radio-resistance. Internalized EGFR can also be transported from the cell surface to several intracellular compartments, such as the Golgi apparatus, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the mitochondria, in addition to the nucleus. In this review, we will summarize the functions of nuclear EGFR family and the potential pathways by which EGFR is trafficked from the cell surface to a variety of cellular organelles. A better understanding of the molecular mechanism of EGFR trafficking will shed light on both the receptor biology and potential therapeutic targets of anti-EGFR therapies for clinical application.
Figures
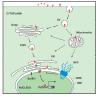
References
-
- Avraham R, Yarden Y. Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:104–117. - PubMed
-
- Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Lo HW, Hsu SC, Hung MC. EGFR signaling pathway in breast cancers: from traditional signal transduction to direct nuclear translocalization. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;95:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Huang PH, Xu AM, White FM. Oncogenic EGFR signaling networks in glioma. Sci Signal. 2009;2:6. - PubMed
-
- Irmer D, Funk JO, Blaukat A. EGFR kinase domain mutations - functional impact and relevance for lung cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2007;26:5693–5701. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

