Toll-like receptor (TLR) and inflammasome actions in the central nervous system
- PMID: 22521509
- PMCID: PMC3383346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2012.03.001
Toll-like receptor (TLR) and inflammasome actions in the central nervous system
Abstract
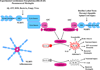
During the past 10 years, much attention has been focused towards elucidating the impact of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in central nervous system (CNS) innate immunity. TLR signaling triggers the transcriptional activation of pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β) and pro-IL-18 that are processed into their active forms by the inflammasome. Recent studies have demonstrated inflammasome involvement during CNS infection, autoimmune disease, and injury. This review will address inflammasome actions within the CNS and how cooperation between TLR and inflammasome signaling may influence disease outcome. In addition, the concept of alternative inflammasome functions independent of IL-1 and IL-18 processing are considered in the context of CNS disease.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Greenwood J, et al. Review: leucocyte-endothelial cell crosstalk at the blood-brain barrier: a prerequisite for successful immune cell entry to the brain. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37:24–39. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Schroder K, Tschopp J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140:821–832. - PubMed
-
- Petrilli V, et al. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:1583–1589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

