Sex dimorphism in the association of cardiometabolic characteristics and osteophytes-defined radiographic knee osteoarthritis among obese and non-obese adults: NHANES III
- PMID: 22521953
- PMCID: PMC3595163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.02.644
Sex dimorphism in the association of cardiometabolic characteristics and osteophytes-defined radiographic knee osteoarthritis among obese and non-obese adults: NHANES III
Abstract
Objective: To examine the relationship of knee osteoarthritis (OA) with cardiovascular and metabolic risk factors by obesity status and gender.
Methods: Data from 1,066 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III participants (≥60 years of age) was used to examine relationships of osteophytes-defined radiographic knee OA and cardiovascular and metabolic measures. Analyses were considered among obese [body mass index (BMI)≥30 kg/m(2)] and non-obese (BMI<30 kg/m(2)) men and women.
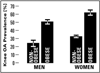
Results: The prevalence of osteophytes-defined radiographic knee OA was 34%. Leptin levels and homeostatic model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), a proxy measure of insulin resistance, were significantly associated with knee OA; those with knee OA had 35% higher HOMA-IR values and 52% higher leptin levels compared to those without knee OA. The magnitude of the association between HOMA-IR and knee OA was strongest among men, regardless of obesity status; odds ratios (ORs) for HOMA-IR were 34% greater among non-obese men (OR=1.18) vs obese women (OR=0.88). Among obese women, a 5-μg/L higher leptin was associated with nearly 30% higher odds of having knee OA (OR=1.28). Among men, ORs for the association of leptin and knee OA were in the opposite direction.
Conclusions: Cardiometabolic dysfunction is related to osteophytes-defined radiographic knee OA prevalence and persists within subgroups defined by obesity status and gender. A sex dimorphism in the direction and magnitude of cardiometabolic risk factors with respect to knee OA was described including HOMA-IR being associated with OA prevalence among men while leptin levels were most important among women.
Copyright © 2012 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any financial conflicts of interest to report.
Figures


Comment in
-
Osteoarthritis and the metabolic syndrome: more evidence that the etiology of OA is different in men and women.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012 Jul;20(7):603-4. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.04.007. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012. PMID: 22521952 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Helmick CG, Felson DT, Lawrence RC, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Kwoh CK, et al. for the National Arthritis Data Workgroup. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part I. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:15–25. - PubMed
-
- Sowers M, Jannausch ML, Gross M, Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Palmieri RM, Crutchfield M, et al. Performance-based physical functioning in African-American and Caucasian women at midlife: considering body composition, quadriceps strength, and knee osteoarthritis. Am J Epidemiol. 2006;163:950–958. - PubMed
-
- Ling SM, Fried LP, Garrett ES, Fan MY, Rantanen T, Bathon JM. Knee osteoarthritis comprises early mobility function: the Women’s Health and Aging Study II. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:114–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

