IgG4-Related Perineural Disease
- PMID: 22523496
- PMCID: PMC3317227
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/401890
IgG4-Related Perineural Disease
Abstract
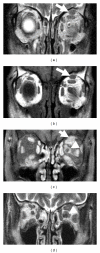
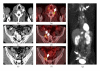
Aims. To elucidate characteristics of IgG4-related disease involving the peripheral nervous system. Methods. Retrospective review of 106 patients with IgG4-related disease identified 21 peripheral nerve lesions in 7 patients. Clinicopathological and radiological features were examined. Results. Peripheral nerve lesions were commonly identified in orbital or paravertebral area, involving orbital (n = 9), optic (n = 4), spinal (n = 7), and great auricular nerves (n = 1). The predominant radiological feature was a distinct perineural soft tissue mass, ranging 8 to 30 mm in diameter. Histologically, the epineurium was preferentially involved by massive lymphoplasmacytic infiltration rich in IgG4(+) plasma cells. All lesions were neurologically asymptomatic and steroid-responsive at the first presentation, but one recurrent lesion around the optic nerve caused failing vision. Conclusion. IgG4-related disease of the peripheral nervous system is characterized by orbital or paravertebral localization, perineural mass formation, and rare neurologic symptoms. The term "IgG4-related perineural disease" seems appropriate to describe this entity.
Figures



References
-
- Kitagawa S, Zen Y, Harada K, et al. Abundant IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration characterizes chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Küttner's tumor) American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2005;29(6):783–791. - PubMed
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344(10):732–738. - PubMed
-
- Zen Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, et al. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis with and without hepatic inflammatory pseudotumor, and sclerosing pancreatitis-associated sclerosing cholangitis: do they belong to a spectrum of sclerosing pancreatitis? American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2004;28(9):1193–1203. - PubMed
-
- Cornell LD, Chicano SL, Deshpande V, et al. Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2007;31(10):1586–1597. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

