Air pollution, oxidative stress, and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22523504
- PMCID: PMC3317180
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/472751
Air pollution, oxidative stress, and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
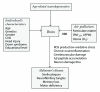
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia affecting millions of people worldwide and will continue to affect millions more with population aging on the rise. AD causality is multifactorial. Known causal factors include genetic predisposition, age, and sex. Environmental toxins such as air pollution (AP) have also been implicated in AD causation. Exposure to AP can lead to chronic oxidative stress (OS), which is involved in the pathogenesis of AD. Whereas AP plays a role in AD pathology, the epidemiological evidence for this association is limited. Given the significant prevalence of AP exposure combined with increased population aging, epidemiological evidence for this link is important to consider. In this paper, we examine the existing evidence supporting the relationship between AP, OS, and AD and provide recommendations for future research on the population level, which will provide evidence in support of public health interventions.
Figures
References
-
- Bird TD. Alzheimer’s disease overview. In: Pagon R, Bird T, Dolan CR, editors. Gene Reviews. Seattle, Wash, USA: University of Washington; 1998.
-
- Hebert LE, Scherr PA, Bienias JL, Bennett DA, Evans DA. Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Archives of Neurology. 2003;60(8):1119–1122. - PubMed
-
- Wimo A, Jonsson L, Winblad B. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and direct costs of dementia in 2003. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. 2006;21(3):175–181. - PubMed
-
- Saunders A, Strittmatter W, Schmechel D, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele E4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1993;43(8):1467–1472. - PubMed
-
- Coon KD, Myers AJ, Craig DW, et al. A high-density whole-genome association study reveals that APOE is the major susceptibility gene for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2007;68(4):613–618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

