Nonlinear dynamics in cardiology
- PMID: 22524390
- PMCID: PMC3733460
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071811-150106
Nonlinear dynamics in cardiology
Abstract
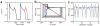
The dynamics of many cardiac arrhythmias, as well as the nature of transitions between different heart rhythms, have long been considered evidence of nonlinear phenomena playing a direct role in cardiac arrhythmogenesis. In most types of cardiac disease, the pathology develops slowly and gradually, often over many years. In contrast, arrhythmias often occur suddenly. In nonlinear systems, sudden changes in qualitative dynamics can, counterintuitively, result from a gradual change in a system parameter-this is known as a bifurcation. Here, we review how nonlinearities in cardiac electrophysiology influence normal and abnormal rhythms and how bifurcations change the dynamics. In particular, we focus on the many recent developments in computational modeling at the cellular level that are focused on intracellular calcium dynamics. We discuss two areas where recent experimental and modeling work has suggested the importance of nonlinearities in calcium dynamics: repolarization alternans and pacemaker cell automaticity.
Figures
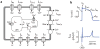




References
-
- Fink M, Niederer SA, Cherry EM, Fenton FH, Koivumäki JT, et al. Cardiac cell modelling: observations from the heart of the cardiac physiome project. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011;104:2–21. - PubMed
-
- Zaniboni M, Pollard AE, Yang L, Spitzer KW. Beat-to-beat repolarization variability in ventricular myocytes and its suppression by electrical coupling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;278:H677–87. - PubMed
-
- Zaniboni M. 3D current-voltage-time surfaces unveil critical repolarization differences underlying similar cardiac action potentials: A model study. Mathematical Biosciences. 2011;233:98–110. - PubMed
-
- Bányász T, Horváth B, Virág L, Bárándi L, Szentandrássy N, et al. Reverse rate dependency is an intrinsic property of canine cardiac preparations. Cardiovasc Res. 2009;84:237–44. - PubMed
-
- Pastore JM, Girouard SD, Laurita KR, Akar FG, Rosenbaum DS. Mechanism linking T-wave alternans to the genesis of cardiac fibrillation. Circulation. 1999;99:1385–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

