Exposure to violence during childhood is associated with telomere erosion from 5 to 10 years of age: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 22525489
- PMCID: PMC3616159
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2012.32
Exposure to violence during childhood is associated with telomere erosion from 5 to 10 years of age: a longitudinal study
Abstract
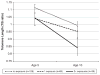
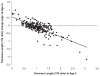
There is increasing interest in discovering mechanisms that mediate the effects of childhood stress on late-life disease morbidity and mortality. Previous studies have suggested one potential mechanism linking stress to cellular aging, disease and mortality in humans: telomere erosion. We examined telomere erosion in relation to children's exposure to violence, a salient early-life stressor, which has known long-term consequences for well-being and is a major public-health and social-welfare problem. In the first prospective-longitudinal study with repeated telomere measurements in children while they experienced stress, we tested the hypothesis that childhood violence exposure would accelerate telomere erosion from age 5 to age 10 years. Violence was assessed as exposure to maternal domestic violence, frequent bullying victimization and physical maltreatment by an adult. Participants were 236 children (49% females; 42% with one or more violence exposures) recruited from the Environmental-Risk Longitudinal Twin Study, a nationally representative 1994-1995 birth cohort. Each child's mean relative telomere length was measured simultaneously in baseline and follow-up DNA samples, using the quantitative PCR method for T/S ratio (the ratio of telomere repeat copy numbers to single-copy gene numbers). Compared with their counterparts, the children who experienced two or more kinds of violence exposure showed significantly more telomere erosion between age-5 baseline and age-10 follow-up measurements, even after adjusting for sex, socioeconomic status and body mass index (B=-0.052, s.e.=0.021, P=0.015). This finding provides support for a mechanism linking cumulative childhood stress to telomere maintenance, observed already at a young age, with potential impact for life-long health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wegman HL, Stetler C. A meta-analytic review of the effects of childhood abuse on medical outcomes in adulthood. Psychosom Med. 2009;71:805– 812. - PubMed
-
- Dong M, Giles WH, Felitti VJ, Dube SR, Williams JE, Chapman DP, et al. Insights into causal pathways for ischemic heart disease: adverse childhood experiences study. Circulation. 2004;110:1761– 1766. - PubMed
-
- Nanni V, Uher R, Danese A. Childhood maltreatment predicts unfavorable course of illness and treatment outcome in depression: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry. 2012;169:141– 151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources