In vivo gene delivery by nonviral vectors: overcoming hurdles?
- PMID: 22525514
- PMCID: PMC3392980
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2012.79
In vivo gene delivery by nonviral vectors: overcoming hurdles?
Abstract
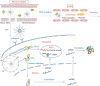
The promise of cancer gene therapeutics is hampered by difficulties in the in vivo delivery to the targeted tumor cells, and systemic delivery remains to be the biggest challenge to be overcome. Here, we concentrate on systemic in vivo gene delivery for cancer therapy using nonviral vectors. In this review, we summarize the existing delivery barriers together with the requirements and strategies to overcome these problems. We will also introduce the current progress in the design of nonviral vectors, and briefly discuss their safety issues.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

