Randomized study on early detection of lung cancer with MSCT in Germany: study design and results of the first screening round
- PMID: 22526165
- PMCID: PMC12443666
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-012-1228-9
Randomized study on early detection of lung cancer with MSCT in Germany: study design and results of the first screening round
Abstract
Purpose: Low-dose multislice-CT (MSCT) detects many early-stage lung cancers with good prognosis, but whether it decreases lung cancer mortality and at which costs is yet insufficiently explored. Scope of the present study is to examine within a common European effort whether MSCT screening is capable to reduce the lung cancer mortality by at least 20 % and at which amount of undesired side effects this could be achieved.
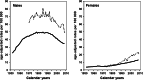
Methods: Overall 4,052 heavy smoking men and women were recruited by a population-based approach and randomized into a screening arm with five annual MSCT screens and an initial quit-smoking counseling, and a control arm with initial quit-smoking counseling and five annual questionnaire inquiries.
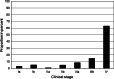
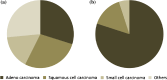
Results: In the first screening round, 2,029 participants received a MSCT providing 1,488 negative and 540 suspicious screens with early recalls (early recall rate 26.6 %) leading to 31 biopsies (biopsy rate 1.5 %) and 22 confirmed lung cancers (detection rate 1.1 %). Among the lung cancers, 15 were adenocarcinomas, 3 squamous cell carcinomas, one small-cell lung cancer, and 3 others, whereby 18 were in clinical stage I, one in stage II, and 3 in stage III. One interval cancer occurred.
Conclusions: The indicated performance indicators fit into the range observed in comparable trials. The study continues finalizing the second screening round and for the first participants even the last screening round. The unresolved issue of the precise amount of side effects and the high early recall rate precludes currently the recommendation of MSCT as screening tool for lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Bach PB, Kelley MJ, Tate RC, McCrory DC (2003) Screening for lung cancer. A review of the current literature. Chest 123:72s–82s - PubMed
-
- Bach PB, Jett JR, Pastorino U, Tockman MS, Swensen SJ, Begg CB (2007) Computed tomography screening and lung cancer outcomes. JAMA 297:953–961 - PubMed
-
- Diederich S, Thomas M, Semik M, Lenzen H, Roos N, Weber A, Heindel W, Wormanns D (2004) Screening for early lung cancer with low-dose spiral computed tomography: results of annual follow-up examinations in asymptomatic smokers. Eur Radiol 14:691–702 - PubMed
-
- Henschke CI, McCauley DI, Yankelevitz DF, Naidich DP, McGuiness G, Miettinen OS, Libby DM, Pasmantier MW, Koizumi J, Altorki NK, Smith JP (1999) Early lung cancer action project: overall design and findings from baseline screening. The Lancet 354:99–105 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

