In vivo expression of angiotensin-(1-7) lowers blood pressure and improves baroreflex function in transgenic (mRen2)27 rats
- PMID: 22526299
- PMCID: PMC3419797
- DOI: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182588b32
In vivo expression of angiotensin-(1-7) lowers blood pressure and improves baroreflex function in transgenic (mRen2)27 rats
Abstract
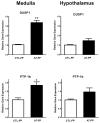
Transgenic (mRen2)27 rats are hypertensive with impaired baroreflex sensitivity for control of heart rate compared with Hannover Sprague-Dawley rats. We assessed blood pressure and baroreflex function in male hemizygous (mRen2)27 rats (30-40 weeks of age) instrumented for arterial pressure recordings and receiving into the cisterna magna either an Ang-(1-7) fusion protein or a control fusion protein (CTL-FP). The maximum reduction in mean arterial pressure achieved was -38 ± 7 mm Hg on day 3, accompanied by a 55% enhancement in baroreflex sensitivity in Ang-(1-7) fusion protein-treated rats. Both the high-frequency alpha index (HF-α) and heart rate variability increased, suggesting increased parasympathetic tone for cardiac control. The mRNA levels of several components of the renin-angiotensin system in the dorsal medulla were markedly reduced including renin (-80%), neprilysin (-40%), and the AT1a receptor (-40%). However, there was a 2-fold to 3-fold increase in the mRNA levels of the phosphatases PTP-1b and dual-specificity phosphatase 1 in the medulla of Ang-(1-7) fusion protein-treated rats. Our finding that replacement of Ang-(1-7) in the brain of (mRen2)27 rats reverses in part the hypertension and baroreflex impairment is consistent with a functional deficit of Ang-(1-7) in this hypertensive strain. We conclude that the increased mRNA expression of phosphatases known to counteract the phosphoinositol 3 kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinases, and the reduction of renin and AT1a receptor mRNA levels may contribute to the reduction in arterial pressure and improvement in baroreflex sensitivity in response to Ang-(1-7).
Conflict of interest statement
No relationships to disclose.
Figures







References
-
- Mullins JJ, Peters J, Ganten D. Fulminant hypertension in transgenic rats harbouring the mouse Ren-2 gene. Nature. 1990;344:541–544. - PubMed
-
- Barrett GL, Mullins JJ. Studies on blood pressure regulation in hypertensive Ren-2 transgenic rats. Kidney Int. 1992;41(Suppl.37):S-125–S-128. - PubMed
-
- Moriguchi A, Brosnihan KB, Kumagai H, Ganten D, Ferrario CM. Mechanisms of hypertension in transgenic rats expressing the mouse Ren-2 gene. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:R1273–R1278. - PubMed
-
- Senanayake PD, Moriguchi A, Kumagai H, Ganten D, Ferrario CM, Brosnihan KB. Increased expression of angiotensin peptides in the brain of transgenic hypertensive rats. Peptides. 1994;15:919–926. - PubMed
-
- Moriguchi A, Tallant EA, Matsumura K, Reilly TM, Walton H, Ganten D, Ferrario CM. Opposing actions of Angiotensin-(1-7) and Angiotensin II in the brain of transgenic hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1995;25:1260–1265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

