Genetic features of cerebrospinal fluid-derived subtype B HIV-1 tat
- PMID: 22528397
- PMCID: PMC3572198
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-011-0059-9
Genetic features of cerebrospinal fluid-derived subtype B HIV-1 tat
Abstract
Since HIV-1 Tat has been associated with neurocognitive dysfunction, we investigated 60 HIV-1 subtype B-infected individuals who were characterized for neurocognitive functioning and had paired CSF and blood plasma samples available. To avoid issues with repeated sampling, we generated population-based HIV-1 tat sequences from each compartment and evaluated these data using a battery of phylogenetic, statistical, and machine learning tools. These analyses identified position HXB2 5905 within the cysteine-rich domain of tat as a signature of CSF-derived HIV-1, and a higher number of mixed bases in CSF, as measure of diversity, was associated with HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder. Since identified mutations were synonymous, we evaluated the predicted secondary RNA structures, which showed that this mutation altered secondary structure. As a measure of divergence, the genetic distance between the blood and CSF-derived tat was inversely correlated with current and nadir CD4+ T cell counts. These data suggest that specific HIV-1 features of tat influence neurotropism and neurocognitive impairment.
Figures
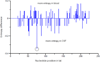

References
-
- Antinori A, Arendt G, Becker JT, Brew BJ, Byrd DA, Cherner M, Clifford DB, Cinque P, Epstein LG, Goodkin K, Gisslen M, Grant I, Heaton RK, Joseph J, Marder K, Marra CM, McArthur JC, Nunn M, Price RW, Pulliam L, Robertson KR, Sacktor N, Valcour V, Wojna VE. Updated research nosology for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology. 2007;69:1789–1799. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baliga G, Case J, Jain S, Suraj M. Machine Learning of Higher-Order Programs. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 1992;620:9–20.
-
- Bayer P, Kraft M, Ejchart A, Westendorp M, Frank R, Rosch P. Structural studies of HIV-1 Tat protein. J Mol Biol. 1995;247:529–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19AI090970/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI077304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI36214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH083552/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI043638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH62512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI080353/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI74621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI080353/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 MH022005/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083552/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI077304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI090970/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI074621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

