ATP synthesis and storage
- PMID: 22528680
- PMCID: PMC3360099
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-012-9305-8
ATP synthesis and storage
Abstract
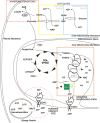
Since 1929, when it was discovered that ATP is a substrate for muscle contraction, the knowledge about this purine nucleotide has been greatly expanded. Many aspects of cell metabolism revolve around ATP production and consumption. It is important to understand the concepts of glucose and oxygen consumption in aerobic and anaerobic life and to link bioenergetics with the vast amount of reactions occurring within cells. ATP is universally seen as the energy exchange factor that connects anabolism and catabolism but also fuels processes such as motile contraction, phosphorylations, and active transport. It is also a signalling molecule in the purinergic signalling mechanisms. In this review, we will discuss all the main mechanisms of ATP production linked to ADP phosphorylation as well the regulation of these mechanisms during stress conditions and in connection with calcium signalling events. Recent advances regarding ATP storage and its special significance for purinergic signalling will also be reviewed.
Figures


References
-
- Pollard-Knight D, Cornish-Bowden A. Mechanism of liver glucokinase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982;44(2):71–80. - PubMed
-
- Robey RB, Hay N. Mitochondrial hexokinases: guardians of the mitochondria. Cell Cycle. 2005;4(5):654–658. - PubMed
-
- Sirover MA. New insights into an old protein: the functional diversity of mammalian glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1432(2):159–184. - PubMed
-
- Jurica MS, et al. The allosteric regulation of pyruvate kinase by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Structure. 1998;6(2):195–210. - PubMed
-
- Mazurek S (2011) Pyruvate kinase type M2: A key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:969–980 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

