Laurdan generalized polarization fluctuations measures membrane packing micro-heterogeneity in vivo
- PMID: 22529342
- PMCID: PMC3358851
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1118288109
Laurdan generalized polarization fluctuations measures membrane packing micro-heterogeneity in vivo
Abstract
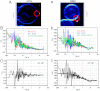
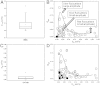
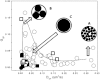
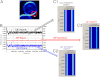
Cellular membranes are heterogeneous in composition, and the prevailing theory holds that the structures responsible for this heterogeneity in vivo are small structures (10-200 nm), sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched, of different sizes, highly dynamic denominated rafts. Rafts are postulated to be platforms, which by sequestering different membrane components can compartmentalize cellular processes and regulate signaling pathways. Despite an enormous effort in this area, the existence of these domains is still under debate due to the characteristics of the structures itself: small in size and highly mobile, which from the technical point of view implies using techniques with high spatial and temporal resolution. In this report we measured rapid fluctuations of the normalized ratio of the emission intensity at two wavelengths of Laurdan, a membrane fluorescent dye sensitive to local membrane packing. We observed generalized polarization fluctuations in the plasma membrane of intact rabbit erythrocytes and Chinese hamster ovary cells that can be explained by the existence of tightly packed micro-domains moving in a more fluid background phase. These structures, which display different lipid packing, have different sizes; they are found in the same cell and in the entire cell population. The small size and characteristic high lipid packing indicate that these micro-domains have properties that have been proposed for lipid rafts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pike LJ. Rafts defined: A report on the keystone symposium on lipid rafts and cell function. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:1597–1598. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson K, Mouritsen OG, Anderson RGW. Lipid rafts: At a crossroad between cell biology and physics. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:7–14. - PubMed
-
- He H-T, Marguet D. Detecting nanodomains in living cell membrane by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Annu Rev Phys Chem. 2011;62:417–436. - PubMed
-
- Smith SK, et al. Mechanisms by which intracellular calcium induces susceptibility to secretory phospholipase a2 in human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:22732–22741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

