Data management in clinical research: An overview
- PMID: 22529469
- PMCID: PMC3326906
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.93842
Data management in clinical research: An overview
Abstract
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is a critical phase in clinical research, which leads to generation of high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data from clinical trials. This helps to produce a drastic reduction in time from drug development to marketing. Team members of CDM are actively involved in all stages of clinical trial right from inception to completion. They should have adequate process knowledge that helps maintain the quality standards of CDM processes. Various procedures in CDM including Case Report Form (CRF) designing, CRF annotation, database designing, data-entry, data validation, discrepancy management, medical coding, data extraction, and database locking are assessed for quality at regular intervals during a trial. In the present scenario, there is an increased demand to improve the CDM standards to meet the regulatory requirements and stay ahead of the competition by means of faster commercialization of product. With the implementation of regulatory compliant data management tools, CDM team can meet these demands. Additionally, it is becoming mandatory for companies to submit the data electronically. CDM professionals should meet appropriate expectations and set standards for data quality and also have a drive to adapt to the rapidly changing technology. This article highlights the processes involved and provides the reader an overview of the tools and standards adopted as well as the roles and responsibilities in CDM.
Keywords: Clinical data interchange standards consortium; clinical data management systems; data management; e-CRF; good clinical data management practices; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

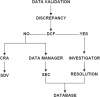
References
-
- Lu Z, Su J. Clinical data management: Current status, challenges, and future directions from industry perspectives. Open Access J Clin Trials. 2010;2:93–105.
-
- CFR - Code of Federal Regulations Title 21 [Internet] Maryland: Food and Drug Administration. [Updated 2010 Apr 4; Cited 2011 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr... .
-
- Study Data Tabulation Model [Internet] Texas: Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium. c2011. [Updated 2007 Jul; Cited 2011 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.cdisc.org/sdtm .
-
- CDASH [Internet] Texas: Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium. c2011. [Updated 2011 Jan; Cited 2011 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.cdisc.org/cdash .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

