Pharmacist glycemic control team improves quality of glycemic control in surgical patients with perioperative dysglycemia
- PMID: 22529756
- PMCID: PMC3327108
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/11-131
Pharmacist glycemic control team improves quality of glycemic control in surgical patients with perioperative dysglycemia
Abstract
Context: Perioperative hyperglycemia is a risk factor for increased morbidity and mortality. Improved glycemic control has been demonstrated to reduce surgical site infections, reduce perioperative morbidity, and reduce length of stay. However, safe and effective perioperative glycemic control can be limited by expert clinician availability.
Objective: To improve quality by reliably providing safe and effective glycemic control to surgical patients with diabetes or stress hyperglycemia.
Design: A designated group of pharmacists, the Glycemic Control Team (GCT), worked under protocol, on a consultation basis, to manage perioperative dysglycemia during hospitalization. We used a pre-post, observational study design to assess the effectiveness of the intervention and implementation of the GCT.
Main outcome measures: The proportion of patients pre- and postintervention with good glycemic control and with hypoglycemia were measured and compared. We defined good glycemic control as having all, or all but one, point-of-care blood glucose values between 70-180 mg/dL in each 24-hour period. We defined hypoglycemia as having any point-of-care test glucose value <70 mg/dL in any of the 3 days evaluated.
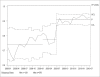
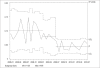
Results: During the preimplementation period, 77.4% of postoperative patient days demonstrated good glycemic control. In the postimplementation period, this percentage increased to 90.3%. Over the same period, the rate of hypoglycemia decreased from 8.6% to 4.6%.
Conclusion: Implementation of a pharmacist team to manage glycemic control in hospitalized, postoperative patients led to safer and better quality of glycemic care as measured by improved glycemic control and lower rates of hypoglycemia.
Figures
References
-
- Ramos M, Khalpey Z, Lipsitz S, et al. Relationship of perioperative hyperglycemia and postoperative infections in patients who undergo general and vascular surgery. Ann Surg. 2008 Oct;248(4):585–91. - PubMed
-
- Estrada CA, Young JA, Nifong LW, Chitwood WR., Jr. Outcomes and perioperative hyperglycemia in patients with or without diabetes mellitus undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003 May;75(5):1392–9. - PubMed
-
- Furnary AP, Gao G, Grunkemeier GL, et al. Continuous insulin infusion reduces mortality in patients with diabetes undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003 May;125(5):1007–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

