Spontaneous lumbar curve correction in selective anterior instrumentation and fusion of idiopathic thoracic scoliosis of Lenke type C
- PMID: 22531898
- PMCID: PMC3616460
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-012-2299-7
Spontaneous lumbar curve correction in selective anterior instrumentation and fusion of idiopathic thoracic scoliosis of Lenke type C
Abstract
Background: Posterior pedicle screw instrumented correction and fusion have become the gold standard in the surgical treatment of thoracic scoliosis. However, in thoracic Lenke type C curves selective posterior fusion of the thoracic curve may lead to spinal imbalance. The aim of the study was to analyse the radiological results of selective anterior thoracic fusion using a standard open dual rod technique with special respect to spontaneous lumbar curve correction (SLCC).
Methods: Twenty-eight patients (26 patients with Lenke 1C and 2 patients with Lenke 2C curves) with an average age of 15 years were surgically treated with an anterior dual rod system through a standard open double thoracotomy approach. Average clinical and radiological follow-up was 4 years (24-84 months).
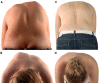
Results: Fusion was carried out mostly from end-to-end vertebra. The primary curve was corrected from 61.6° (average correction on reverse bending films 42.9 %) to 27.1° (56.0 % correction) with an average loss of correction of 2.2°. The secondary lumbar curve measured 47.7° preoperatively (40-56°, average correction on reverse bending films 66.2 %) and corrected spontaneously to 30.1° (36 % SLCC) and remained stable without any cases of deterioration or decompensation during follow-up. Lumbar apical vertebral translation increased minimally by an average of 4 mm directly, postoperatively, and returned to an average of preoperative values during follow-up. All but two curves remained as type C lumbar modifier at follow-up. Preoperatively, three patients showed a marked coronal imbalance of more than 3 cm (all left, average 4.0 cm); at follow-up, two patients were still out of balance by more than 3 cm (all to the left, average 3.4 cm). Preoperatively, a marked shoulder imbalance of more than 1.0 cm was found in 11 patients; this was corrected in all patients to <1.0 cm at follow-up. The apical vertebral rotation measured according to Perdriolle was corrected from 23.5° to 15.0° in the thoracic spine (36.2 % correction) with an average clinical reduction of the rib hump of 63.2 %. In the lumbar spine, there was no relevant radiological derotation; however, clinically, the lumbar hump corrected spontaneously by 44.3 %. Thoracic kyphosis measured 28.5° preoperatively and 32.3° at follow-up. All six patients with a preoperative hypokyphosis (<20°) of an average of 9.5° were successfully corrected to an average thoracic kyphosis of 23.8° at follow-up. There were no cases of junctional thoracolumbar kyphosis. There were neither reoperations nor implant failures with pseudarthrosis.
Conclusion: Selective anterior correction and fusion in primary thoracic curves with lumbar modifier type Lenke C resulted in a reliable and satisfactory SLCC. Advantages of anterior versus posterior techniques are the true segmental derotation with excellent rib hump correction and a superior restoration of thoracic kyphosis.
Figures



References
-
- Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, et al. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic scoliosis. Spine. 1995;20:1399–1405. - PubMed
-
- Lenke LG, Betz RR, Harms J, et al. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a new classification to determine extent of arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001;83A:1169–1181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

