Analysis of a membrane-enriched proteome from postmortem human brain tissue in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22532456
- PMCID: PMC3338199
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201100068
Analysis of a membrane-enriched proteome from postmortem human brain tissue in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Purpose: The present study is a discovery mode proteomics analysis of the membrane-enriched fraction of postmortem brain tissue from Alzheimer's disease (AD) and control cases. This study aims to validate a method to identify new proteins that could be involved in the pathogenesis of AD and potentially serve as disease biomarkers.
Experimental design: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) was used to analyze the membrane-enriched fraction of human postmortem brain tissue from five AD and five control cases of similar age. Biochemical validation of specific targets was performed by immunoblotting.
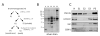
Results: One thousand seven hundred and nine proteins were identified from the membrane-enriched fraction of frontal cortex. Label-free quantification by spectral counting and G-test analysis identified 13 proteins that were significantly changed in disease. In addition to Tau (MAPT), two additional proteins found to be enriched in AD, ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase 1 (UCHL1), and syntaxin-binding protein 1 (Munc-18), were validated through immunoblotting. DISCUSSION AND CLINICAL RELEVANCE: Proteomic analysis of the membrane-enriched fraction of postmortem brain tissue identifies proteins biochemically altered in AD. Further analysis of this subproteome may help elucidate mechanisms behind AD pathogenesis and provide new sources of biomarkers.
© 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



References
-
- International, A. s. D. World Alzheimer Report 2009. 2009;92
-
- Goedert M, Spillantini MG. A century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 2006;314:777–781. - PubMed
-
- Association, A. s. Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 2011;Volume 7 2011. - PubMed
-
- Daviglus ML, Bell CC, Berrettini W, Bowen PE, et al. National Institutes of Health State-of-the-Science Conference Statement: Preventing Alzheimer Disease and Cognitive Decline. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2010;153:176–181. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2006;368:387–403. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

