Tuning the properties of elastin mimetic hybrid copolymers via a modular polymerization method
- PMID: 22533503
- PMCID: PMC3372701
- DOI: 10.1021/bm3002705
Tuning the properties of elastin mimetic hybrid copolymers via a modular polymerization method
Abstract
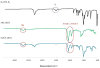
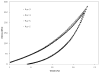
We have synthesized elastin mimetic hybrid polymers (EMHPs) via the step-growth polymerization of azide-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and alkyne-terminated peptide (AKAAAKA)(2) (AK2) that is abundant in the cross-linking domains of the natural elastin. The modular nature of our synthesis allows facile adjustment of the peptide sequence to modulate the structural and biological properties of EMHPs. Therefore, EMHPs containing cell-binding domains (CBDs) were constructed from α,ω-azido-PEG and two types of alkyne-terminated AK2 peptides with sequences of DGRGX(AKAAAKA)(2)X (AK2-CBD1) and X(AKAAAKA)(2)XGGRGDSPG (AK2-CBD2, X = propargylglycine) via a step-growth, click coupling reaction. The resultant hybrid copolymers contain an estimated five to seven repeats of PEG and AK2 peptides. The secondary structure of EMHPs is sensitive to the specific sequence of the peptidic building blocks, with CBD-containing EMHPs exhibiting a significant enhancement in the α-helical content as compared with the peptide alone. Elastomeric hydrogels formed by covalent cross-linking of the EMHPs had a compressive modulus of 1.06 ± 0.1 MPa. Neonatal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDFs) were able to adhere to the hydrogels within 1 h and to spread and develop F-actin filaments 24 h postseeding. NHDF proliferation was only observed on hydrogels containing RGDSP domains, demonstrating the importance of integrin engagement for cell growth and the potential use of these EMHPs as tissue engineering scaffolds. These cell-instructive, hybrid polymers are promising candidates as elastomeric scaffolds for tissue engineering.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Elastin-Mimetic Hybrid Polymers with Multiblock, Alternating Molecular Architecture and Elastomeric Properties.Macromolecules. 2009 Apr;42(7):2532-2541. doi: 10.1021/ma802791z. Macromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19763157 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembly of block copolymers derived from elastin-mimetic polypeptide sequences.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002 Oct 18;54(8):1057-73. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00059-5. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002. PMID: 12384307 Review.
-
Self-assembly and photo-cross-linking of eight-armed PEG-PTMC star block copolymers.Biomacromolecules. 2011 Jul 11;12(7):2746-54. doi: 10.1021/bm200515h. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Biomacromolecules. 2011. PMID: 21630632
-
Synthesis and self-assembly of well-defined elastin-like polypeptide-poly(ethylene glycol) conjugates.Biomacromolecules. 2014 Jul 14;15(7):2751-9. doi: 10.1021/bm5006195. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Biomacromolecules. 2014. PMID: 24945908
-
Resilin-PEG Hybrid Hydrogels Yield Degradable Elastomeric Scaffolds with Heterogeneous Microstructure.Biomacromolecules. 2016 Jan 11;17(1):128-40. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01255. Epub 2015 Dec 22. Biomacromolecules. 2016. PMID: 26646060 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biomaterials-based strategies for salivary gland tissue regeneration.Biomater Sci. 2016 Apr;4(4):592-604. doi: 10.1039/c5bm00358j. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Biomater Sci. 2016. PMID: 26878077 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Formation from Hybrid, Multiblock Copolymers of Poly(Acrylic Acid) and VPGVG Peptide.Soft Matter. 2013 Feb 7;9(5):1589-1599. doi: 10.1039/C2SM27496E. Soft Matter. 2013. PMID: 23976897 Free PMC article.
-
Opportunities for multicomponent hybrid hydrogels in biomedical applications.Biomacromolecules. 2015 Jan 12;16(1):28-42. doi: 10.1021/bm501361c. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Biomacromolecules. 2015. PMID: 25426888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meter-long multiblock copolymer microfibers via interfacial bioorthogonal polymerization.Adv Mater. 2015 May 6;27(17):2783-90. doi: 10.1002/adma.201500360. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Adv Mater. 2015. PMID: 25824805 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Synthesis of Biomimetic Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering.Polym Int. 2017 Dec;66(12):1787-1799. doi: 10.1002/pi.5407. Epub 2017 May 26. Polym Int. 2017. PMID: 31080322 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

