Neuroprotection by inhibiting the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway after cerebral ischemia occurs independently of interleukin-6 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC/CXCL1) secretion
- PMID: 22533966
- PMCID: PMC3416579
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-76
Neuroprotection by inhibiting the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway after cerebral ischemia occurs independently of interleukin-6 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC/CXCL1) secretion
Abstract
Background: Cerebral ischemia is associated with the activation of glial cells, infiltration of leukocytes and an increase in inflammatory mediators in the ischemic brain and systemic circulation. How this inflammatory response influences lesion size and neurological outcome remains unclear. D-JNKI1, an inhibitor of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway, is strongly neuroprotective in animal models of stroke. Intriguingly, the protection mediated by D-JNKI1 is high even with intravenous administration at very low doses with undetectable drug levels in the brain, pointing to a systemic mode of action, perhaps on inflammation.
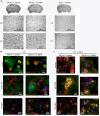
Findings: We evaluated whether D-JNKI1, administered intravenously 3 h after the onset of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), modulates secretion of the inflammatory mediators interleukin-6 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine in the plasma and from the spleen and brain at several time points after MCAO. We found an early release of both mediators in the systemic circulation followed by an increase in the brain and went on to show a later systemic increase in vehicle-treated mice. Release of interleukin-6 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine from the spleen of mice with MCAO was not significantly different from sham mice. Interestingly, the secretion of these inflammatory mediators was not altered in the systemic circulation or brain after successful neuroprotection with D-JNKI1.
Conclusions: We demonstrate that neuroprotection with D-JNKI1 after experimental cerebral ischemia is independent of systemic and brain release of interleukin-6 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine. Furthermore, our findings suggest that the early systemic release of interleukin-6 and keratinocyte-derived chemokine may not necessarily predict an unfavorable outcome in this model.
Figures

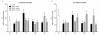
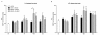
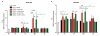
References
-
- Emsley HCA, Smith CJ, Gavin CM, Georgiou RF, Vail A, Barberan EM, Hallenbeck JM, del Zoppo GJ, Rothwell NJ, Tyrrell PJ, Hopkins SJ. An early and sustained peripheral inflammatory response in acute ischaemic stroke: relationships with infection and atherosclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2003;139:93–101. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5728(03)00134-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smith CJ, Emsley HCA, Gavin CM, Georgiou RF, Vail A, Barberan EM, del Zoppo GJ, Hallenbeck JM, Rothwell NJ, Hopkins SJ, Tyrrell PJ. Peak plasma interleukin-6 and other peripheral markers of inflammation in the first week of ischaemic stroke correlate with brain infarct volume, stroke severity and long-term outcome. BMC Neurology. 2004;4:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-4-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McColl BW, Rothwell NJ, Allan SM. Systemic inflammatory stimulus potentiates the acute phase and CXC chemokine responses to experimental stroke and exacerbates brain damage via interleukin-1- and neutrophil-dependent mechanisms. J Neurosci. 2007;27:4403–4412. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5376-06.2007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kyriakis JM, Avruch J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:9807–9869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

