A novel role for type 1 angiotensin receptors on T lymphocytes to limit target organ damage in hypertension
- PMID: 22534490
- PMCID: PMC3393036
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.261768
A novel role for type 1 angiotensin receptors on T lymphocytes to limit target organ damage in hypertension
Abstract
Rationale: Human clinical trials using type 1 angiotensin (AT(1)) receptor antagonists indicate that angiotensin II is a critical mediator of cardiovascular and renal disease. However, recent studies have suggested that individual tissue pools of AT(1) receptors may have divergent effects on target organ damage in hypertension.
Objective: We examined the role of AT(1) receptors on T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of hypertension and its complications.
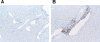
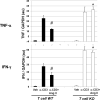
Methods and results: Deficiency of AT(1) receptors on T cells potentiated kidney injury during hypertension with exaggerated renal expression of chemokines and enhanced accumulation of T cells in the kidney. Kidneys and purified CD4(+) T cells from "T cell knockout" mice lacking AT(1) receptors on T lymphocytes had augmented expression of Th1-associated cytokines including interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α. Within T lymphocytes, the transcription factors T-bet and GATA-3 promote differentiation toward the Th1 and Th2 lineages, respectively, and AT(1) receptor-deficient CD4(+) T cells had enhanced T-bet/GATA-3 expression ratios favoring induction of the Th1 response. Inversely, mice that were unable to mount a Th1 response due to T-bet deficiency were protected from kidney injury in our hypertension model.
Conclusions: The current studies identify an unexpected role for AT(1) receptors on T lymphocytes to protect the kidney in the setting of hypertension by favorably modulating CD4(+) T helper cell differentiation.
Figures
















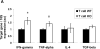
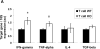
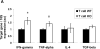
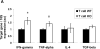
Comment in
-
Studies of the T-cell angiotensin receptor using cre-lox technology: an unan-T-cellpated result.Circ Res. 2012 Jun 8;110(12):1543-5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.271411. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22679135 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360:1903–1913. - PubMed
-
- Dahlof B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Beevers G, de Faire U, Fyhrquist F, Ibsen H, Kristiansson K, Lederballe-Pedersen O, Lindholm LH, Nieminen MS, Omvik P, Oparil S, Wedel H. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the losartan intervention for endpoint reduction in hypertension study (life): A randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet. 2002;359:995–1003. - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Muller DN, Shagdarsuren E, Park JK, Dechend R, Mervaala E, Hampich F, Fiebeler A, Ju X, Finckenberg P, Theuer J, Viedt C, Kreuzer J, Heidecke H, Haller H, Zenke M, Luft FC. Immunosuppressive treatment protects against angiotensin ii-induced renal damage. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:1679–1693. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

