DNA ends alter the molecular composition and localization of Ku multicomponent complexes
- PMID: 22535209
- PMCID: PMC3412971
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.013581
DNA ends alter the molecular composition and localization of Ku multicomponent complexes
Abstract
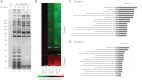
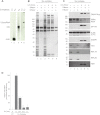
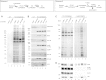
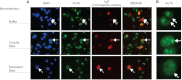
The Ku heterodimer plays an essential role in non-homologous end-joining and other cellular processes including transcription, telomere maintenance and apoptosis. While the function of Ku is regulated through its association with other proteins and nucleic acids, the specific composition of these macromolecular complexes and their dynamic response to endogenous and exogenous cellular stimuli are not well understood. Here we use quantitative proteomics to define the composition of Ku multicomponent complexes and demonstrate that they are dramatically altered in response to UV radiation. Subsequent biochemical assays revealed that the presence of DNA ends leads to the substitution of RNA-binding proteins with DNA and chromatin associated factors to create a macromolecular complex poised for DNA repair. We observed that dynamic remodeling of the Ku complex coincided with exit of Ku and other DNA repair proteins from the nucleolus. Microinjection of sheared DNA into live cells as a mimetic for double strand breaks confirmed these findings in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Calsou P., Delteil C., Frit P., Drouet J., Salles B. (2003) Coordinated assembly of Ku and p460 subunits of the DNA-dependent protein kinase on DNA ends is necessary for XRCC4-ligase IV recruitment. J. Mol. Biol. 326, 93–103 - PubMed
-
- Ma Y., Lu H., Tippin B., Goodman M. F., Shimazaki N., Koiwai O., Hsieh C. L., Schwarz K., Lieber M. R. (2004) A biochemically defined system for mammalian nonhomologous DNA end joining. Mol. Cell 16, 701–713 - PubMed
-
- Meek K., Gupta S., Ramsden D. A., Lees-Miller S. P. (2004) The DNA-dependent protein kinase: the director at the end. Immunol. Rev. 200, 132–141 - PubMed
-
- Chibazakura T., Watanabe F., Kitajima S., Tsukada K., Yasukochi Y., Teraoka H. (1997) Phosphorylation of human general transcription factors TATA-binding protein and transcription factor IIB by DNA-dependent protein kinase–synergistic stimulation of RNA polymerase II basal transcription in vitro. Eur. J. Biochem. 247, 1166–1173 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

