Wnt/Wingless signaling in Drosophila
- PMID: 22535229
- PMCID: PMC3367557
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a007930
Wnt/Wingless signaling in Drosophila
Abstract
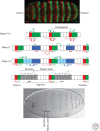
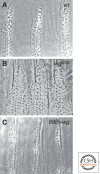
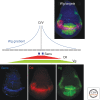
The Wingless (Wg) pathway represents one of the best-characterized intercellular signaling networks. Studies performed in Drosophila over the last 30 years have contributed to our understanding of the role of Wg signaling in the regulation of tissue growth, polarity, and patterning. These studies have revealed mechanisms conserved in the vertebrate Wnt pathways and illustrate the elegance of using the Drosophila model to understand evolutionarily conserved modes of gene regulation. In this article, we describe the function of Wg signaling in patterning the Drosophila embryonic epidermis and wing imaginal disc. As well, we present an overview of the establishment of the Wg morphogen gradient and discuss the differential modes of Wg-regulated gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Affolter M, Pyrowolakis G, Weiss A, Basler K 2008. Signal-induced repression: The exception or the rule in developmental signaling? Dev Cell 15: 11–22 - PubMed
-
- Alexandre C, Lecourtois M, Vincent J 1999. Wingless and Hedgehog pattern Drosophila denticle belts by regulating the production of short-range signals. Development 126: 5689–5698 - PubMed
-
- Babu P 1977. Early developmental subdivisions of the wing disk in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet 151: 289–294 - PubMed
-
- Baeg GH, Lin X, Khare N, Baumgartner S, Perrimon N 2001. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are critical for the organization of the extracellular distribution of Wingless. Development 128: 87–94 - PubMed
-
- Baeg GH, Selva EM, Goodman RM, Dasgupta R, Perrimon N 2004. The Wingless morphogen gradient is established by the cooperative action of Frizzled and Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan receptors. Dev Biol 276: 89–100 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
