Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in transplantation and cancer
- PMID: 22535241
- PMCID: PMC4000733
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-012-8335-1
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in transplantation and cancer
Abstract
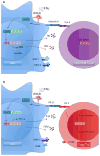
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) are myeloid cells that suppress the immune response, a definition that reflects both their origin and their function. As negative regulators of the immune response, MDSC represent a novel therapeutic approach for manipulating the immune system toward tolerance or immunity. MDSC are present in cancer patients and tumor-bearing mice and are in part responsible for the inhibition of the cell-mediated immune response against the tumor. Our laboratories investigate the immunologic mechanisms of tumor acceptance mediated by MDSC, which can be exploited to prevent allograft rejection in transplantation. A better understanding of MDSC biology will open new avenues for therapeutic intervention, either by inhibiting their function (i.e. in cancer patients), or by enhancing their suppressive effects and promoting their expansion (i.e. in organ transplantation and alloimmune responses). In this review, we summarize some of the critical aspects of the immunoregulatory function of MDSC in cancer and transplantation and discuss their potential clinical applications.
Figures


References
-
- Kamo I, Friedman H. Immunosuppression and the role of suppressive factors in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1977;25:271–321. - PubMed
-
- Kirchner H, Holden HT, Herberman RB. Splenic suppressor macrophages induced in mice by injection of Corynebacterium parvum. J Immunol. 1975;115:1212–6. - PubMed
-
- Dugast AS, Haudebourg T, Coulon F, Heslan M, Haspot F, Poirier N, Vuillefroy de Silly R, Usal C, Smit H, Martinet B, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells accumulate in kidney allograft tolerance and specifically suppress effector T cell expansion. J Immunol. 2008;180:7898–906. - PubMed
-
- Argyris BF. Suppressor factor produced by neonatal mouse spleen cells. Cell Immunol. 1981;62:412–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

