Pharmacokinetic interactions between the hormonal emergency contraception, levonorgestrel (Plan B), and Efavirenz
- PMID: 22536010
- PMCID: PMC3299227
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/137192
Pharmacokinetic interactions between the hormonal emergency contraception, levonorgestrel (Plan B), and Efavirenz
Abstract
Objectives: Compare the Plan B levonorgestrel (LNG) area under the concentration- time curve (AUC(12)) prior to and with efavirenz (EFV). Design. Prospective, open-label, single-arm, equivalence study.
Methods: Healthy HIV-negative subjects underwent 12 hr intensive pharmacokinetic (PK) sampling following single dose LNG alone and after 14 days of EFV. Geometric means, Geometric Mean Ratios, and 90% confidence intervals (CI) are reported for PK Parameters. T-tests were utilized. Clinical parameters and liver function tests (LFTs) were assessed.
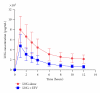
Results: 24 women enrolled and 21 completed the study. With EFV, LNG AUC(12) was reduced 56% (95% CI: 49%, 62%) from 42.9 to 17.8 ng∗hr/mL, and maximum concentration (C(max)) was reduced 41% (95% CI: 33%, 50%) from 8.4 to 4.6 ng/mL. LNG was well tolerated with no grade 3 or 4 treatment-related toxicities.
Conclusions: EFV significantly reduced LNG exposures. Higher LNG doses may be required with EFV. These results reinforce the importance of effective contraception in women taking EFV.
Figures
References
-
- HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report. Cases of HIV and AIDS in the United States and Dependent Areas. 2007.
-
- UNAIDS. AIDS Epidemic Update: December 2005.
-
- Sustiva (Efavirenz) Capsule and Tablets.US Prescribing Information. Princeton, NJ, USA: Bristol-Myers-Squibb; 2010.
-
- Saitoh A, Hull AD, Franklin P, Spector SA. Myelomeningocele in an infant with intrauterine exposure to efavirenz. Journal of Perinatology. 2005;25(8):555–556. - PubMed
-
- Fundarò C, Genovese O, Rendeli C, Tamburrini E, Salvaggio E. Myelomeningocele in a child with intrauterine exposure to efavirenz. AIDS. 2002;16(2):299–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical