A laccase with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activity from the broth of mycelial culture of the mushroom Lentinus tigrinus
- PMID: 22536022
- PMCID: PMC3321470
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/536725
A laccase with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activity from the broth of mycelial culture of the mushroom Lentinus tigrinus
Abstract
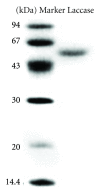
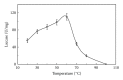
A 59 kDa laccase with inhibitory activity against HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (IC(50) = 2.4 μM) was isolated from the broth of mycelial culture of the mushroom Lentinus tigrinus. The isolation procedure involved ion exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose and CM-cellulose, and gel filtration by fast protein liquid chromatography on Superdex 75. The laccase was adsorbed on both types of ion exchangers. About 95-fold purification was achieved with a 25.9% yield of the enzyme. The procedure resulted in a specific enzyme activity of 76.6 U/mg. Its N-terminal amino acid sequence was GIPDLHDLTV, which showed little similarity to other mushroom laccase and other Lentinus tigrinus strain laccase. Its characteristics were different from previously reported laccase of other Lentinus tigrinus strain. Maximal laccase activity was observed at a pH of 4 and at a temperature of 60°C, respectively. This study yielded the information about the potentially exploitable activities of Lentinus tigrinus laccase.
Figures



References
-
- Reinhammar B. Purification and properties of laccase and stellacyanin from Rhus vernicifera. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1970;205(1):35–47. - PubMed
-
- Mayer AM, Staples RC. Laccase: new functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry. 2002;60(6):551–565. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins TL, Kramer KJ. Insect cuticle sclerotization. Annual Review of Entomology. 1992;37(1):273–302.
-
- Alexandre G, Zhulin IB. Laccases are widespread in bacteria. Trends in Biotechnology. 2000;18(2):41–42. - PubMed
-
- Claus H. Laccases and their occurrence in prokaryotes. Archives of Microbiology. 2003;179(3):145–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

