Two new reference materials based on tobacco leaves: certification for over a dozen of toxic and essential elements
- PMID: 22536124
- PMCID: PMC3334301
- DOI: 10.1100/2012/216380
Two new reference materials based on tobacco leaves: certification for over a dozen of toxic and essential elements
Abstract
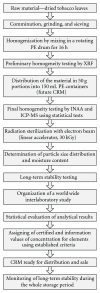
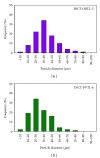
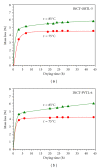
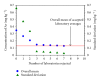
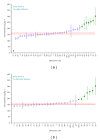
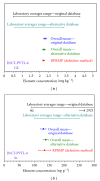
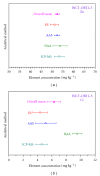
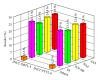
The preparation, certification, and characterization of two new biological certified reference materials for inorganic trace analysis have been presented. They are based on two different varieties of tobacco leaves, namely, Oriental Basma Tobacco Leaves (INCT-OBTL-5), grown in Greece, and Polish Virginia Tobacco Leaves (INCT-PVTL-6), grown in Poland. Certification of the materials was based on the statistical evaluation of results obtained in a worldwide interlaboratory comparison, in which 87 laboratories from 18 countries participated, providing 2568 laboratory averages on nearly 80 elements. It was possible to establish the certified values of concentration for many elements in the new materials, that is, 37 in INCT-OBTL-5 and 36 in INCT-PVTL-6, including several toxic ones like As, Cd, Hg, Pb, and so forth. The share and the role of instrumental analytical techniques used in the process of certification of the new CRMs are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Some difficult problems still existing in the preparation and certification of CRMs.Fresenius J Anal Chem. 2001 Jun;370(2-3):126-30. doi: 10.1007/s002160100722. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 2001. PMID: 11451222
-
Preparation and use of reference materials for quality assurance in inorganic trace analysis.Food Addit Contam. 2002 Oct;19(10):928-38. doi: 10.1080/0265203021000011791. Food Addit Contam. 2002. PMID: 12443554
-
Multielement trace determination in SiC powders: assessment of interlaboratory comparisons aimed at the validation and standardization of analytical procedures with direct solid sampling based on ETV ICP OES and DC arc OES.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005 Dec;383(7-8):1060-74. doi: 10.1007/s00216-005-3415-x. Epub 2005 Aug 4. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2005. PMID: 16079974
-
Trends in certified reference materials for the speciation of trace elements.Fresenius J Anal Chem. 2001 Jun;370(2-3):120-5. doi: 10.1007/s002160100709. Fresenius J Anal Chem. 2001. PMID: 11451221 Review.
-
[Reference materials and trace element analysis].Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1995;31(2):255-9. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 1995. PMID: 8561389 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Elements including metals in the atomizer and aerosol of disposable electronic cigarettes and electronic hookahs.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 17;12(4):e0175430. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175430. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28414730 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental Metabarcoding Reveals Contrasting Belowground and Aboveground Fungal Communities from Poplar at a Hg Phytomanagement Site.Microb Ecol. 2017 Nov;74(4):795-809. doi: 10.1007/s00248-017-0984-0. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Microb Ecol. 2017. PMID: 28451743
-
Gustatory receptor neurons in Manduca sexta contain a TrpA1-dependent signaling pathway that integrates taste and temperature.Chem Senses. 2013 Sep;38(7):605-17. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt032. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Chem Senses. 2013. PMID: 23828906 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Effect of ZnO and CeO2 Nanoparticles on Pisum sativum L.: A Photosynthesis and Nutrients Uptake Study.Cells. 2021 Nov 10;10(11):3105. doi: 10.3390/cells10113105. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831328 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Element Composition of Diatom Chaetoceros spp. from Natural Phytoplankton Assemblages of the Russian Arctic Seas.Biology (Basel). 2021 Oct 8;10(10):1009. doi: 10.3390/biology10101009. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2008. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
-
- WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2009. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
-
- Skwarzec B, Ulatowski J, Strumińska DI, Boryło A. Inhalation of 210Po and 210Pb from cigarette smoking in Poland. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity. 2001;57(3):221–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

