Functional requirements for inhibitory signal transmission by the immunomodulatory receptor CD300a
- PMID: 22537350
- PMCID: PMC3418551
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-23
Functional requirements for inhibitory signal transmission by the immunomodulatory receptor CD300a
Abstract
Background: Activation signals can be negatively regulated by cell surface receptors bearing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs). CD300a, an ITIM bearing type I transmembrane protein, is expressed on many hematopoietic cells, including subsets of lymphocytes.
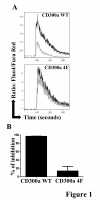
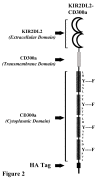
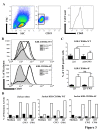
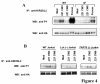
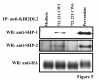
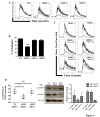
Results: We have taken two approaches to further define the mechanism by which CD300a acts as an inhibitor of immune cell receptor signaling. First, we have expressed in Jurkat T cells a chimeric receptor consisting of the extracellular domains of killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR)2DL2 fused to the transmembrane and cytoplasmic segments of CD300a (KIR-CD300a) to explore surrogate ligand-stimulated inhibition of superantigen stimulated T cell receptor (TCR) mediated cell signaling. We found that intact CD300a ITIMs were essential for inhibition and that the tyrosine phosphorylation of these ITIMs required the src tyrosine kinase Lck. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the CD300a ITIMs created docking sites for both src homology 2 domain containing protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-1 and SHP-2. Suppression of SHP-1 and SHP-2 expression in KIR-CD300a Jurkat T cells with siRNA and the use of DT40 chicken B cell lines expressing CD300a and deficient in several phosphatases revealed that SHP-1, but not SHP-2 or the src homology 2 domain containing inositol 5' phosphatase SHIP, was utilized by CD300a for its inhibitory activity.
Conclusion: These studies provide new insights into the function of CD300a in tuning T and B cell responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of antigen-receptor signaling by Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (CD31) requires functional ITIMs, SHP-2, and p56(lck).Blood. 2001 Apr 15;97(8):2351-7. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.8.2351. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11290597
-
Differential roles of N- and C-terminal immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs during inhibition of cell activation by killer cell inhibitory receptors.J Immunol. 1999 Mar 15;162(6):3168-75. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10092767
-
CD300a and CD300f differentially regulate the MyD88 and TRIF-mediated TLR signalling pathways through activation of SHP-1 and/or SHP-2 in human monocytic cell lines.Immunology. 2012 Mar;135(3):226-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03528.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22043923 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors: Immune checkpoint proteins and tumor sustaining factors.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(1):25-40. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1121324. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26636629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitory leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors in cancer development.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Dec;58(12):1216-25. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4925-1. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26566804 Review.
Cited by
-
The CD300 molecules: an emerging family of regulators of the immune system.Blood. 2013 Mar 14;121(11):1951-60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-09-435057. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23293083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Effect of Cytomegalovirus Infection with Age on the Expression of CD57, CD300a, and CD161 on T-Cell Subpopulations.Front Immunol. 2017 Jun 2;8:649. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00649. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28626460 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Cytokines That Enhance Antigen Responsiveness of Naïve CD8+ T Lymphocytes Modulate Chromatin Accessibility of Genes Impacted by Antigen Stimulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 16;23(22):14122. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214122. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430600 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial fluid proteome in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Proteomics. 2016 Jun 5;13:12. doi: 10.1186/s12014-016-9113-1. eCollection 2016. Clin Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27274716 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Expression of CD300a Inhibitory Receptor on CD4+ T Cells From Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1-Infected Patients: Association With Disease Progression Markers.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 23;9:1709. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01709. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30083165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tarasenko T, Dean JA, Bolland S. FcgammaRIIB as a modulator of autoimmune disease susceptibility. Autoimmunity. 2007;40:409–417. - PubMed
-
- Bolland S, Ravetch JV. Inhibitory pathways triggered by ITIM-containing receptors. Adv Immunol. 1999;72:149–177. - PubMed
-
- Campbell KS, Colonna M. Human natural killer cell receptors and signal transduction. Int Rev Immunol. 2001;20:333–370. - PubMed
-
- Daeron M, Jaeger S, Du Pasquier L, Vivier E. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs: a quest in the past and future. Immunol Rev. 2008;224:11–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

