Discovering cytokines as targets for chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 22537849
- PMCID: PMC3512191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.03.027
Discovering cytokines as targets for chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
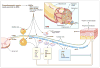
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN), a dose-limiting neurotoxic effect of chemotherapy, is the most common reason for early cessation of cancer treatment. This can result in an increased risk of recurrence and decreased survival rate. Inflammatory cascade activation, proinflammatory cytokine upregulation, and neuro-immune communication pathways play essential roles in the initiation and progression of CIPN. Most notably, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and CCL2 are involved in neuropathic pain. Further elucidation of the role of these cytokines could lead to their development and use as biomarkers for predicting the onset of painful peripheral neuropathy and early axonal damage. In this review, we provide evidence for the involvement of cytokines in CIPN, the possible underlying mechanisms, and their use as potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers to prevent and improve the painful peripheral neuropathy related to chemotherapeutic agents.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Aghajanian C, et al. Phase II study of “dose-dense” high-dose chemotherapy treatment with peripheral-blood progenitor-cell support as primary treatment for patients with advanced ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:1852–60. - PubMed
-
- Cocconi G, et al. Mature results of a prospective randomized trial comparing a three-weekly with an accelerated weekly schedule of cisplatin in advanced ovarian carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999;22:559–67. - PubMed
-
- Pasini F, Durante E, De Manzoni D, Rosti G, Pelosi G. High-dose chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002;22:3465–72. - PubMed
-
- Mielke S, Sparreboom A, Mross K. Peripheral neuropathy: a persisting challenge in paclitaxel-based regimes. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:24–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

