A cardiac microRNA governs systemic energy homeostasis by regulation of MED13
- PMID: 22541436
- PMCID: PMC3340581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.029
A cardiac microRNA governs systemic energy homeostasis by regulation of MED13
Abstract
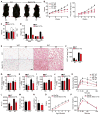
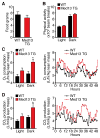
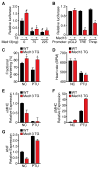
Obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart failure are associated with aberrant cardiac metabolism. We show that the heart regulates systemic energy homeostasis via MED13, a subunit of the Mediator complex, which controls transcription by thyroid hormone and other nuclear hormone receptors. MED13, in turn, is negatively regulated by a heart-specific microRNA, miR-208a. Cardiac-specific overexpression of MED13 or pharmacologic inhibition of miR-208a in mice confers resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity and improves systemic insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance. Conversely, genetic deletion of MED13 specifically in cardiomyocytes enhances obesity in response to high-fat diet and exacerbates metabolic syndrome. The metabolic actions of MED13 result from increased energy expenditure and regulation of numerous genes involved in energy balance in the heart. These findings reveal a role of the heart in systemic metabolic control and point to MED13 and miR-208a as potential therapeutic targets for metabolic disorders.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Metabolic disorders: Heart microRNA provides new route to metabolic control.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Jun 22;11(7):516. doi: 10.1038/nrd3779. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22722531 No abstract available.
-
More than just an engine: the heart regulates body weight.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 17;111(5):513-5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.276063. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22904039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akoulitchev S, Chuikov S, Reinberg D. TFIIH is negatively regulated by cdk8-containing mediator complexes. Nature. 2000;407:102–106. - PubMed
-
- Balaban RS, Kantor HL, Katz LA, Briggs RW. Relation between work and phosphate metabolite in the in vivo paced mammalian heart. Science. 1986;232:1121–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL077439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR040339/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 DK081185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RL1DK081185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL093039/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL053351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL083371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL061544/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL053351/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024923/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- PL1 DK081182/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

