Association of complete recovery from acute kidney injury with incident CKD stage 3 and all-cause mortality
- PMID: 22541737
- PMCID: PMC3422603
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.03.014
Association of complete recovery from acute kidney injury with incident CKD stage 3 and all-cause mortality
Abstract
Background: There is a gap of knowledge in the long-term outcomes of patients who have complete recovery of kidney function after an episode of acute kidney injury (AKI). We sought to determine whether complete recovery of kidney function after an episode of AKI is associated with the development of incident stage 3 chronic kidney disease (CKD) and mortality in patients with normal baseline kidney function.
Design: Retrospective cohort study.
Setting & participants: 3,809 patients from an integrated health care delivery system who had a hospitalization between January 1, 1999, and December 31, 2009, with follow-up through March 31, 2010.
Predictor: AKI defined by International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9) codes and using the AKI Network (AKIN) definition, with complete recovery defined as a decrease in serum creatinine level to less than 1.10 times the baseline value.
Outcomes and measurements: Incident stage 3 CKD persistent for 3 months and all-cause mortality.
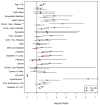
Results: After a median follow-up of 2.5 years, incident stage 3 CKD occurred in 15% and 3% of those with and without AKI, respectively, with an unadjusted HR of 5.93 (95% CI, 4.49-7.84) and HR of 3.82 (95% CI, 2.81-5.19) in propensity score-stratified analyses. Deaths occurred in 35% and 24% of those with and without AKI, respectively, with an unadjusted HR of 1.46 (95% CI, 1.27-1.68). In propensity score-stratified analyses, HR decreased to 1.08 (95% CI, 0.93-1.27).
Limitations: Measurements of albuminuria were not available.
Conclusions: Complete recovery of kidney function after an episode of AKI in patients with normal baseline kidney function is associated with increased risk of the development of incident stage 3 CKD, but not all-cause mortality.
Copyright © 2012 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Acute kidney injury: marker or mediator of subsequent CKD?Am J Kidney Dis. 2013 Jan;61(1):184-5. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.05.028. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013. PMID: 23245738 No abstract available.
References
-
- de Mendonca A, Vincent J, Suter P, et al. Acute Renal Failure in the ICU: Risk Factors and Outcomes Evaluated by the SOFA Score. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26(7):915–921. - PubMed
-
- Groeneveld A, Tran D, van der Meulen, Nauta J, Thijs L. Acute Renal Failure in the Medical Intensive Care Unit: Predisposing, Complicating Factors and Outcome. Nephron. 1991;59(4):602–610. - PubMed
-
- Hobson C, Yavas S, Segal M, et al. Acute Kidney Injury is Associated with Increased Long-term Mortality After Cardiothoracic Surgery. Circulation. 2009;119(18):2444–2453. - PubMed
-
- Bihorac A, Yavas S, Subbiah S, et al. Long-term Risk of Mortality and Acute Kidney Injury During Hospitalization After Major Surgery. Ann Surg. 2009;249(5):851–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

