Effect of glutamate and riluzole on manganese-induced apoptotic cell signaling in neuronally differentiated mouse P19 Cells
- PMID: 22543103
- PMCID: PMC3387314
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.04.015
Effect of glutamate and riluzole on manganese-induced apoptotic cell signaling in neuronally differentiated mouse P19 Cells
Abstract
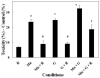
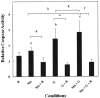
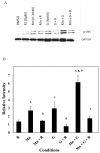
Excess exposure to Mn causes a neurological disorder known as manganism which is similar to dystonic movements associated with Parkinson's disease. Manganism is largely restricted to occupations in which high atmospheric levels are prevalent which include Mn miners, welders and those employed in the ferroalloy processing or related industrial settings. T1 weighted MRI images reveal that Mn is deposited to the greatest extent in the globus pallidus, an area of the brain that is presumed to be responsible for the major CNS associated symptoms. Neurons within the globus pallidus receive glutamatergic input from the subthalamic nuclei which has been suggested to be involved in the toxic actions of Mn. The neurotoxic actions of Mn and glutamate are similar in that they both affect calcium accumulation in the mitochondria leading to apoptotic cell death. In this paper, we demonstrate that the combination of Mn and glutamate potentiates toxicity of neuronally differentiated P19 cells over that observed with either agent alone. Apoptotic signals ROS, caspase 3 and JNK were increased in an additive fashion when the two neurotoxins were combined. The anti-glutamatergic drug, riluzole, was shown to attenuate these apoptotic signals and prevent P19 cell death. Results of this study confirm, for the first time, that Mn toxicity is potentiated in the presence of glutamate and that riluzole is an effective antioxidant which protects against both Mn and glutamate toxicity.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The protective effects of riluzole on manganese-induced disruption of glutamate transporters and glutamine synthetase in the cultured astrocytes.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012 Aug;148(2):242-9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-012-9365-1. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012. PMID: 22391793
-
Protection against glutamate toxicity through inhibition of the p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in neuronally differentiated P19 cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2001 Aug 1;62(3):283-96. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(01)00665-7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11434901
-
Glutamate release inhibitor, Riluzole, inhibited proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by elevated ROS production.Cancer Lett. 2016 Nov 28;382(2):157-165. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.08.028. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 27612558
-
Iron interactions and other biological reactions mediating the physiological and toxic actions of manganese.Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Jul 1;66(1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00145-x. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12818360 Review.
-
The effects of manganese on glutamate, dopamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid regulation.Neurochem Int. 2006 May-Jun;48(6-7):426-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2005.10.012. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Neurochem Int. 2006. PMID: 16513220 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Riluzole on Cisplatin-induced Ototoxicity.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Jul;23(3):e267-e275. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1676654. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 31360245 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of LRRK2 in control and DAT transfected HEK cells increases manganese-induced oxidative stress and cell toxicity.Neurotoxicology. 2013 Jul;37:100-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 Apr 27. Neurotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 23628791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akamatsu K, Shibata MA, Ito Y, Sohma Y, Azuma H, Otsuki Y. Riluzole induces apoptotic cell death in human prostate cancer cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2195–2204. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin M, Mergler D, Larribe F, Belanger S, Tardif R, Bilodeau L, Hudnell K. Bioindicator and exposure data for a population based study of manganese. Neurotoxicology. 1999;20:343–353. - PubMed
-
- Brouillet EP, Shinobu L, McGarvey U, Hochberg F, Beal MF. Manganese injection into the rat striatum produces excitotoxic lesions by impairing energy metabolism. Exp Neurol. 1993;120:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Chen WC, Cheng HH, Huang CJ, Chou CT, Liu SI, Chen IS, Hsu SS, Chang HT, Huang JK, Jan CR. Effect of riluzole on Ca2+ movement and cytotoxicity in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2006;25:461–469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

