VEGF inhibition, hypertension, and renal toxicity
- PMID: 22544560
- PMCID: PMC3746763
- DOI: 10.1007/s11912-012-0242-z
VEGF inhibition, hypertension, and renal toxicity
Abstract
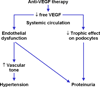
The use of anti-angiogenic agents as part of the therapeutic armamentarium for advanced stage solid tumors has become the standard of care in several instances, particularly for renal cell carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. These agents primarily target vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and/or its receptors, and include bevacizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody against VEGF, as well as tyrosine kinase inhibitors that target several receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK), including VEGF receptors. These therapies, as a general class of anti-angiogenic medications, have been shown to have common adverse vascular effects attributable directly or indirectly to their anti-VEGF effects, including hypertension, renal vascular injury, often manifested by proteinuria and thrombotic microangiopathy, and congestive heart failure. Knowledge of these common side effects and their underlying mechanisms may allow for more accurate and prompt diagnoses, timely clinical interventions, and the development of rational and standard treatments. These measures may minimize patient morbidity and mortality, not only by the treatment of side effects, but also by minimizing the disruption of treatment of the underlying malignancy, as well as improving patient quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–1186. - PubMed
-
- Eremina V, Quaggin SE. Biology of anti-angiogenic therapy-induced thrombotic microangiopathy. Seminars in nephrology. 2010;30:582–590. - PubMed
-
- Eskens FA, Verweij J. The clinical toxicity profile of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) targeting angiogenesis inhibitors a review. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:3127–3139. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Kappers MH, van Esch JH, Sleijfer S, Danser AH, van den Meiracker AH. Cardiovascular and renal toxicity during angiogenesis inhibition: clinical and mechanistic aspects. J Hypertens. 2009;27:2297–2309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

