Rapid development of exhaustion and down-regulation of eomesodermin limit the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred murine natural killer cells
- PMID: 22544698
- PMCID: PMC3382935
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-03-415364
Rapid development of exhaustion and down-regulation of eomesodermin limit the antitumor activity of adoptively transferred murine natural killer cells
Abstract
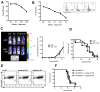
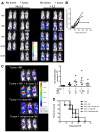
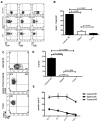
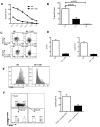
Natural killer (NK) cells are potent anti-viral and antitumor "first responders" endowed with natural cytotoxicity and cytokine production capabilities. To date, attempts to translate these promising biologic functions through the adoptive transfer of NK cells for the treatment of cancer have been of limited benefit. Here we trace the fate of adoptively transferred murine NK cells and make the surprising observation that NK cells traffic to tumor sites yet fail to control tumor growth or improve survival. This dysfunction is related to a rapid down-regulation of activating receptor expression and loss of important effector functions. Loss of interferon (IFN)γ production occurs early after transfer, whereas loss of cytotoxicity progresses with homeostatic proliferation and tumor exposure. The dysfunctional phenotype is accompanied by down-regulation of the transcription factors Eomesodermin and T-bet, and can be partially reversed by the forced overexpression of Eomesodermin. These results provide the first demonstration of NK-cell exhaustion and suggest that the NK-cell first-response capability is intrinsically limited. Further, novel approaches may be required to circumvent the described dysfunctional phenotype.
Figures


References
-
- Cooley S, Gada P, McKenna D, et al. Successful haploidentical hematopoietic cell engraftment using a non-myeloablative preparative regimen including natural killer (NK) cells [abstract]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2008;112 Abstract 827.
-
- Curti A, Ruggeri L, D'Addio A, et al. Successful transfer of alloreactive haploidentical KIR ligand-mismatched natural killer cells after infusion in elderly high-risk acute myeloid leukemia patients. Blood. 2011;118(12):3273–3279. - PubMed
-
- Law T, Motzer R, Mazumdar M. Phase III randomized trial of interleukin-2 with or without lymphokine-activated killer cells in the treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1995;76(5):824–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

