Inflammation markers after randomization to abacavir/lamivudine or tenofovir/emtricitabine with efavirenz or atazanavir/ritonavir
- PMID: 22546988
- PMCID: PMC3560932
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328354f4fb
Inflammation markers after randomization to abacavir/lamivudine or tenofovir/emtricitabine with efavirenz or atazanavir/ritonavir
Abstract
Background: The effect of specific antiretrovirals on inflammation is unclear.
Methods: A5224s was a substudy of A5202, which randomized HIV-infected treatment-naïve patients to blinded abacavir/lamivudine (ABC/3TC) or tenofovir/emtricitabine (TDF/FTC) with open-label efavirenz (EFV) or atazanavir/ritonavir (ATV/r) in a factorial design. Our analysis compared changes in inflammation markers from baseline to week 24 between ABC/3TC and TDF/FTC. Secondary analyses included changes at week 96 and comparisons of EFV vs. ATV/r.
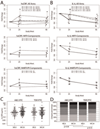
Results: Analyses included 244 patients (85% male, 48% white non-Hispanic), median age 39 years, HIV-1 RNA 4.6 log10 copies/ml, CD4 240 cells/μl. TNF-α, soluble receptors of TNF-α (sTNFR)-I and II, soluble vascular cellular adhesion molecule (sVCAM)-1 and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule (sICAM)-1 decreased significantly at weeks 24 and 96, without significant differences between components (P ≥ 0.44). At week 24, ABC/3TC had a greater high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) mean fold change than TDF/FTC {1.43 vs. 0.88, estimated mean fold change percentage difference [Δ] 61.5% [95% confidence interval (CI) 13.6%, 129.5%]; P = 0.008}. Similar results were seen at week 96 (P = 0.021). At week 24 (but not 96), EFV had a greater hsCRP mean fold change than ATV/r [1.41 vs. 0.88; Δ = 60.2% (12.6%, 127.7%); P = 0.009]. IL-6 decreased significantly at week 24 with TDF/FTC but not with ABC/3TC (between-components P = 0.019). At week 96, IL-6 decreased significantly in both nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor components (between-components P = 0.11). IL-6 changes were not significantly different between ATV/r and EFV at either time point (P ≥ 0.89).
Conclusions: Soluble TNF-receptors and adhesion molecules decreased following treatment initiation and did not differ by regimens. Differences were seen on hsCRP and IL-6 changes with ABC/3TC vs. TDF/FTC and on hsCRP with EFV vs. ATV/r.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts: Grace A McComsey has served as a scientific advisor or speaker for Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Tibotec, and Gilead Sciences, has received research grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and Gilead Sciences, and is currently serving as the DSMB Chair for a Pfizer-sponsored study. Douglas Kitch has no conflict. Eric S. Daar serves as a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, ViiV and receives research grant support from Abbott Laboratories, Merck, Gilead, ViiV, and Pfizer. Camlin Tierney is a member of a DSMB for Tibotec. Nasreen Jahed has no conflict. Kathleen Melbourne is an employee of Gilead Sciences and owns stock in Gilead Sciences. Belinda Ha is an employee of GlaxoSmithKline. Todd Brown has served as a scientific consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Abbott, Tibotec, and Gilead Sciences, has received research grants from GlaxoSmithKline and Merck. Neal Fedarko has no conflict. Anthony Bloom has no conflict. Paul Sax serves as a consultant for Abbott, BMS, Gilead, GSK, Merck, Tibotec, and ViiV and receives grant Support from Gilead, Merck, and Tibotec.
Figures

References
-
- Aukrust P, Muller F, Lien E, Nordoy I, Liabakk NB, Kvale D, et al. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) system levels in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients during highly active antiretroviral therapy: persistent TNF activation is associated with virologic and immunologic treatment failure. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:74–82. - PubMed
-
- Henry K, Kitch D, Dube M, Zackin R, Parker RA, Sprecher D, et al. C-Reactive protein levels over time and cardiovascular risk in HIV-infected individuals suppressed on an indinavir-based regimen: AIDS Clinical Trials Group 5056 s. AIDS. 2004;18:2434–2437. - PubMed
-
- Lundgren J, Neuhaus J, Babiker A, Cooper DA, Duprez D, El-Sadr W, et al. Use of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and risk of myocardial infarction in HIV-infected patients; Strategies for Management of Anti-Retroviral Therapy/INSIGHT; DAD Study Study Groups. AIDS. 2008;22:F12–F24. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI065348/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI38855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI065348/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI060354/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

