Dll4-Notch signaling in Flt3-independent dendritic cell development and autoimmunity in mice
- PMID: 22547652
- PMCID: PMC3348095
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20111615
Dll4-Notch signaling in Flt3-independent dendritic cell development and autoimmunity in mice
Abstract
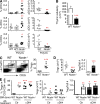
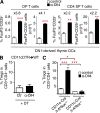
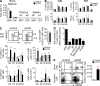
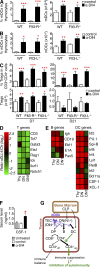
Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4)-Notch signaling is essential for T cell development and alternative thymic lineage decisions. How Dll4-Notch signaling affects pro-T cell fate and thymic dendritic cell (tDC) development is unknown. We found that Dll4 pharmacological blockade induces accumulation of tDCs and CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells (T(reg) cells) in the thymic cortex. Both genetic inactivation models and anti-Dll4 antibody (Ab) treatment promote de novo natural T(reg) cell expansion by a DC-dependent mechanism that requires major histocompatibility complex II expression on DCs. Anti-Dll4 treatment converts CD4(-)CD8(-)c-kit(+)CD44(+)CD25(-) (DN1) T cell progenitors to immature DCs that induce ex vivo differentiation of naive CD4(+) T cells into T(reg) cells. Induction of these tolerogenic DN1-derived tDCs and the ensuing expansion of T(reg) cells are Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (Flt3) independent, occur in the context of transcriptional up-regulation of PU.1, Irf-4, Irf-8, and CSF-1, genes critical for DC differentiation, and are abrogated in thymectomized mice. Anti-Dll4 treatment fully prevents type 1 diabetes (T1D) via a T(reg) cell-mediated mechanism and inhibits CD8(+) T cell pancreatic islet infiltration. Furthermore, a single injection of anti-Dll4 Ab reverses established T1D. Disease remission and recurrence are correlated with increased T(reg) cell numbers in the pancreas-draining lymph nodes. These results identify Dll4-Notch as a novel Flt3-alternative pathway important for regulating tDC-mediated T(reg) cell homeostasis and autoimmunity.
Figures




References
-
- Almeida A.R., Legrand N., Papiernik M., Freitas A.A. 2002. Homeostasis of peripheral CD4+ T cells: IL-2R alpha and IL-2 shape a population of regulatory cells that controls CD4+ T cell numbers. J. Immunol. 169:4850–4860 - PubMed
-
- Anandasabapathy N., Victora G.D., Meredith M., Feder R., Dong B., Kluger C., Yao K., Dustin M.L., Nussenzweig M.C., Steinman R.M., Liu K. 2011. Flt3L controls the development of radiosensitive dendritic cells in the meninges and choroid plexus of the steady-state mouse brain. J. Exp. Med. 208:1695–1705 10.1084/jem.20102657 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

