The super elongation complex family of RNA polymerase II elongation factors: gene target specificity and transcriptional output
- PMID: 22547686
- PMCID: PMC3434493
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00182-12
The super elongation complex family of RNA polymerase II elongation factors: gene target specificity and transcriptional output
Abstract
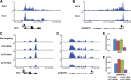
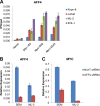
The elongation stage of transcription is highly regulated in metazoans. We previously purified the AFF1- and AFF4-containing super elongation complex (SEC) as a major regulator of development and cancer pathogenesis. Here, we report the biochemical isolation of SEC-like 2 (SEC-L2) and SEC-like 3 (SEC-L3) containing AFF2 and AFF3 in association with P-TEFb, ENL/MLLT1, and AF9/MLLT3. The SEC family members demonstrate high levels of polymerase II (Pol II) C-terminal domain kinase activity; however, only SEC is required for the proper induction of the HSP70 gene upon stress. Genome-wide mRNA-Seq analyses demonstrated that SEC-L2 and SEC-L3 control the expression of different subsets of genes, while AFF4/SEC plays a more dominant role in rapid transcriptional induction in cells. MYC is one of the direct targets of AFF4/SEC, and SEC recruitment to the MYC gene regulates its expression in different cancer cells, including those in acute myeloid or lymphoid leukemia. These findings suggest that AFF4/SEC could be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of leukemia or other cancers associated with MYC overexpression.
Figures
References
-
- Bitoun E, Davies KE. 2005. The robotic mouse: unravelling the function of AF4 in the cerebellum. Cerebellum 4:250–260 - PubMed
-
- Bitoun E, Oliver PL, Davies KE. 2007. The mixed-lineage leukemia fusion partner AF4 stimulates RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation and mediates coordinated chromatin remodeling. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16:92–106 - PubMed
-
- Bursen A, Moritz S, Gaussmann A, Dingermann T, Marschalek R. 2004. Interaction of AF4 wild-type and AF4.MLL fusion protein with SIAH proteins: indication for t(4;11) pathobiology? Oncogene 23:6237–6249 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
