Video games as a complementary therapy tool in mental disorders: PlayMancer, a European multicentre study
- PMID: 22548300
- PMCID: PMC3433177
- DOI: 10.3109/09638237.2012.664302
Video games as a complementary therapy tool in mental disorders: PlayMancer, a European multicentre study
Abstract
Background: Previous review studies have suggested that computer games can serve as an alternative or additional form of treatment in several areas (schizophrenia, asthma or motor rehabilitation). Although several naturalistic studies have been conducted showing the usefulness of serious video games in the treatment of some abnormal behaviours, there is a lack of serious games specially designed for treating mental disorders.
Aim: The purpose of our project was to develop and evaluate a serious video game designed to remediate attitudinal, behavioural and emotional processes of patients with impulse-related disorders.
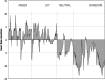
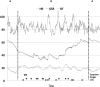
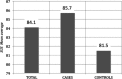
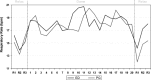
Method and results: The video game was created and developed within the European research project PlayMancer. It aims to prove potential capacity to change underlying attitudinal, behavioural and emotional processes of patients with impulse-related disorders. New interaction modes were provided by newly developed components, such as emotion recognition from speech, face and physiological reactions, while specific impulsive reactions were elicited. The video game uses biofeedback for helping patients to learn relaxation skills, acquire better self-control strategies and develop new emotional regulation strategies. In this article, we present a description of the video game used, rationale, user requirements, usability and preliminary data, in several mental disorders.
Figures

Comment in
-
E-mental health: a medium reaches maturity.J Ment Health. 2012 Aug;21(4):332-5. doi: 10.3109/09638237.2012.682268. Epub 2012 Jun 19. J Ment Health. 2012. PMID: 22712719 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alvarez-Moya E.M., Jimenez-Murcia S., Moragas L., Gomez-Pena M., Aymami M.N., Ochoa C, et al. Executive functioning among female pathological gambling and bulimia nervosa patients: Preliminary findings. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. 2009;15((2)):302–306. - PubMed
-
- Anderson C.A., Sakamoto A., Gentile D.A., Ihori N., Shibuya A., Yukawa S., et al. Longitudinal effects of violent video games on aggression in Japan and the United States. Pediatrics. 2008;122((5)):e1067–1072. - PubMed
-
- APA. DSM-IV-TR: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. (4th ed. Rev.) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000.
-
- Arns M., de Ridder S., Strehl U., Breteler M., Coenen A. Efficacy of neurofeedback treatment in ADHD: The effects on inattention impulsivity and hyperactivity: A meta-analysis. Clinical EEG and Neuroscience. 2009;40((3)):180–189. - PubMed
-
- Barab S., Thomas M., Dodge T., Carteaux R., Tuzun H. Making learning fun: Quest atlantis a game without guns. Educational Technology Research and Development. 2005;53((1)):86–107.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
