Ubiquitylation of the initiator caspase DREDD is required for innate immune signalling
- PMID: 22549468
- PMCID: PMC3380211
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.121
Ubiquitylation of the initiator caspase DREDD is required for innate immune signalling
Abstract
Caspases have been extensively studied as critical initiators and executioners of cell death pathways. However, caspases also take part in non-apoptotic signalling events such as the regulation of innate immunity and activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). How caspases are activated under these conditions and process a selective set of substrates to allow NF-κB signalling without killing the cell remains largely unknown. Here, we show that stimulation of the Drosophila pattern recognition protein PGRP-LCx induces DIAP2-dependent polyubiquitylation of the initiator caspase DREDD. Signal-dependent ubiquitylation of DREDD is required for full processing of IMD, NF-κB/Relish and expression of antimicrobial peptide genes in response to infection with Gram-negative bacteria. Our results identify a mechanism that positively controls NF-κB signalling via ubiquitin-mediated activation of DREDD. The direct involvement of ubiquitylation in caspase activation represents a novel mechanism for non-apoptotic caspase-mediated signalling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

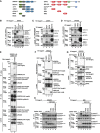


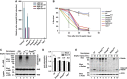

Comment in
-
Innate immunity: regulation of caspases by IAP-dependent ubiquitylation.EMBO J. 2012 Jun 13;31(12):2750-2. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.148. Epub 2012 May 15. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22588080 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen P, Rodriguez A, Erskine R, Thach T, Abrams JM (1998) Dredd, a novel effector of the apoptosis activators reaper, grim, and hid in Drosophila. Dev Biol 201: 202–216 - PubMed
-
- Choe KM, Werner T, Stoven S, Hultmark D, Anderson KV (2002) Requirement for a peptidoglycan recognition protein (PGRP) in Relish activation and antibacterial immune responses in Drosophila. Science 296: 359–362 - PubMed
-
- Chun HJ, Zheng L, Ahmad M, Wang J, Speirs CK, Siegel RM, Dale JK, Puck J, Davis J, Hall CG, Skoda-Smith S, Atkinson TP, Straus SE, Lenardo MJ (2002) Pleiotropic defects in lymphocyte activation caused by caspase-8 mutations lead to human immunodeficiency. Nature 419: 395–399 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

