The p47phox- and NADPH oxidase organiser 1 (NOXO1)-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) mediates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction in a streptozotocin-induced murine model of diabetes
- PMID: 22549734
- PMCID: PMC3694990
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-012-2557-6
The p47phox- and NADPH oxidase organiser 1 (NOXO1)-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) mediates endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction in a streptozotocin-induced murine model of diabetes
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: We have previously shown that NADPH oxidase (NOX) lies upstream of uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), which is known to occur in diabetic endothelium. However, it remains unclear which specific NOX isoform(s) is responsible for eNOS uncoupling and endothelial dysfunction in diabetic mouse models. The aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that one or more NOX isoform(s) mediate(s) diabetic uncoupling of eNOS, which has been shown to occur in patients with diabetes to contribute to endothelial dysfunction.
Methods: Diabetes was induced by streptozotocin administration. The N (ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-sensitive superoxide production of aortic segments, reflective of eNOS uncoupling activity, was determined by electron spin resonance.
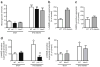
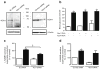
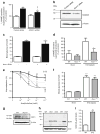
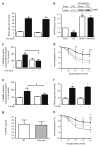
Results: The L-NAME-sensitive superoxide production was more than doubled in wild-type diabetic mice, implicating uncoupling of eNOS. This was abolished in diabetic p47 ( phox-/-) (also known as Ncf1 (-/-)) mice, but preserved in Nox2 (-/y) (also known as Cybb (-/-)) mice made diabetic. The eNOS uncoupling activity was markedly attenuated in diabetic mice transfected with Nox1 or Nox1 organiser 1 (Noxo1) short interfering RNA (siRNA), and abolished in Nox1 (-/y) diabetic mice. Diabetes-induced impairment in endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation was also significantly attenuated in the Nox1 (-/y) mice made diabetic. By contrast, Nox4 siRNA, or inhibition of mitochondrial complex I or III with rotenone or siRNA, respectively, had no effect on diabetic uncoupling of eNOS. Overexpression of Dhfr, or oral administration of folic acid to improve dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) function, recoupled eNOS in diabetes to improve endothelial function.
Conclusions/interpretation: Our data demonstrate for the first time that the p47(phox) and NOXO1-dependent activation of NOX1, but not that of NOX2, NOX4 or mitochondrion, mediates diabetic uncoupling of eNOS. NOX1-null mice are protected from diabetic endothelial dysfunction. Novel approaches to inhibit NOX1 and/or improve DHFR function, may prove to have therapeutic potential for diabetic endothelial dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Harrison DG. Endothelial function and oxidant stress. Clin Cardiol. 1997;20:II-11–II-17. - PubMed
-
- Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res. 2000;87:840–844. - PubMed
-
- Cai H, Griendling KK, Harrison DG. The vascular NAD(P)H oxidases as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:471–478. - PubMed
-
- Hink U, Li H, Mollnau H, et al. Mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circ Res. 2001;88:E14–E22. - PubMed
-
- Oak JH, Cai H. Attenuation of angiotensin II signaling recouples eNOS and inhibits nonendothelial NOX activity in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2007;56:118–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

